Copyright
©2011 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Jan 28, 2011; 17(4): 459-469
Published online Jan 28, 2011. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v17.i4.459
Published online Jan 28, 2011. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v17.i4.459
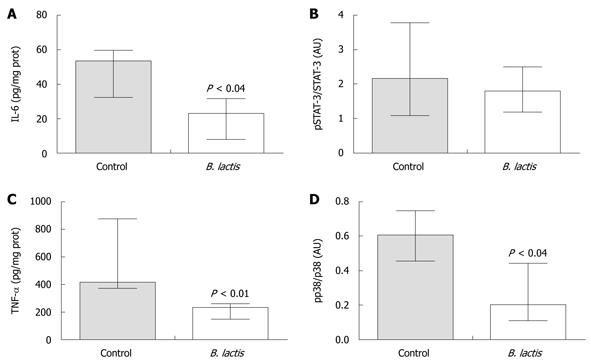
Figure 4 Bifidobacterium lactis feeding significantly diminished protein expression and phosphorylation status of pro-inflammatory markers in colon of recipient mice following adoptive T cell transfer.
Expression of interleukin-6 (IL-6) (A) and tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) (C) protein was measured by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay in colon tissue samples from colitic recipients. The ratios of phosphorylated signal transducer and activator of transcription-3 (pSTAT-3) vs STAT-3 (B) and of pp38 vs p38 (D) were assessed by Western blotting analysis in colon tissue samples of colitic mice. Relative densitometric quantifications of the Western blotting bands are presented. Results are expressed as the mean ± interquartile-range (A and C, n = 5; B, n = 3; and D, n = 4 mice per group) and statistical significance is indicated. B. lactis: Bifidobacterium lactis.
-
Citation: Philippe D, Favre L, Foata F, Adolfsson O, Perruisseau-Carrier G, Vidal K, Reuteler G, Dayer-Schneider J, Mueller C, Blum S.
Bifidobacterium lactis attenuates onset of inflammation in a murine model of colitis. World J Gastroenterol 2011; 17(4): 459-469 - URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v17/i4/459.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v17.i4.459