Copyright
©2011 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Sep 28, 2011; 17(36): 4076-4089
Published online Sep 28, 2011. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v17.i36.4076
Published online Sep 28, 2011. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v17.i36.4076
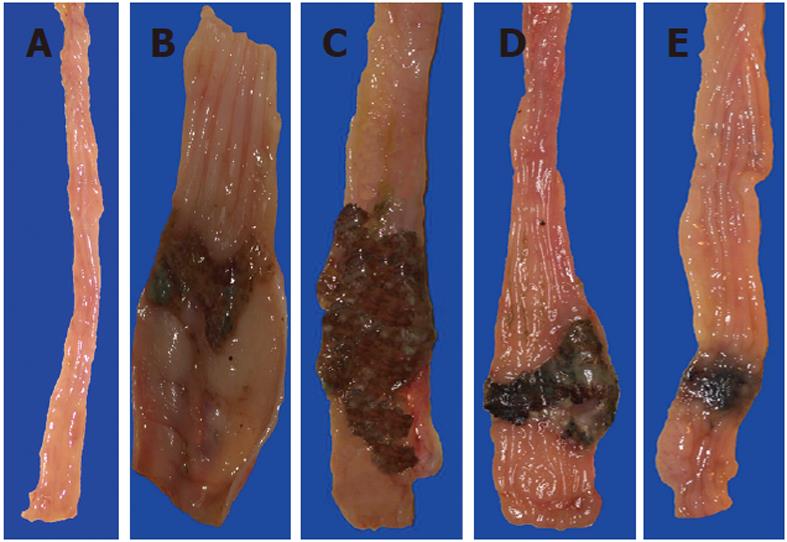
Figure 4 Gross appearance of the intact colon (A), and that of trinitrobenzenesulfonic acid-induced colitis rats treated with vehicle (B), aspirin (C), celecoxib (D) and nitric oxide-aspirin (E) at day 10 of colitis induction.
In aspirin-treated rats (C) the area of colonic damage was larger than in the control trinitrobenzenesulfonic acid rats, which were treated with vehicle (B). In the celecoxib group (D), the area of colonic damage was significantly smaller when compared to the aspirin (ASA) and vehicle groups. The healing of colonic lesions was significantly improved in nitric oxide-ASA treated rats as documented by the small ulceration area and scar formation.
- Citation: Zwolinska-Wcislo M, Brzozowski T, Ptak-Belowska A, Targosz A, Urbanczyk K, Kwiecien S, Sliwowski Z. Nitric oxide-releasing aspirin but not conventional aspirin improves healing of experimental colitis. World J Gastroenterol 2011; 17(36): 4076-4089
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v17/i36/4076.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v17.i36.4076