Copyright
©2011 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Sep 14, 2011; 17(34): 3922-3932
Published online Sep 14, 2011. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v17.i34.3922
Published online Sep 14, 2011. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v17.i34.3922
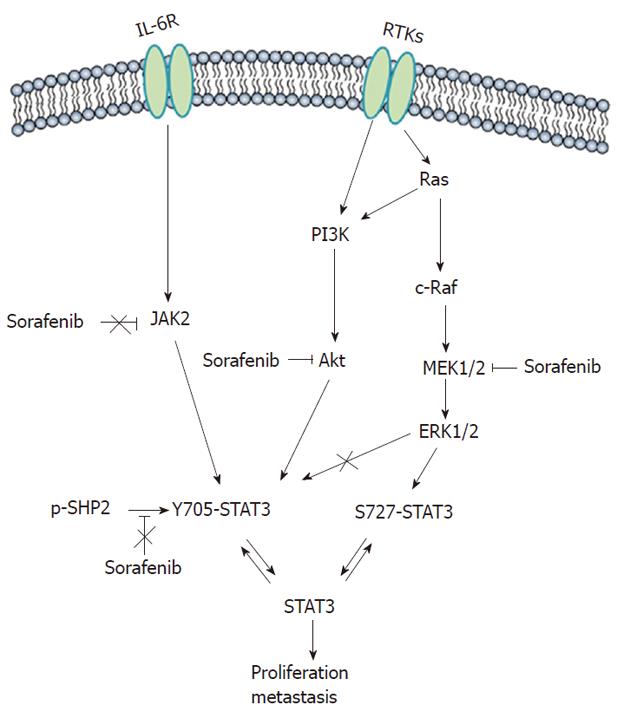
Figure 4 Signaling pathways involved in sorafenib-induced inhibition of signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 phosphorylation.
In hepatocellular carcinoma, extracellular signal-regulated kinase-related pathways regulate signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3) phosphorylation at S727, and phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase (PI3K)/Akt can be responsible for phosphorylation at Y705. Thus, sorafenib inhibits STAT3 phosphorylation in part through blockade of the mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase (MEK)/extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK)/STAT3 and PI3K/Akt/STAT3 signaling pathways, regardless of the Janus kinase 2 and phosphatase shatterproof 2.
- Citation: Gu FM, Li QL, Gao Q, Jiang JH, Huang XY, Pan JF, Fan J, Zhou J. Sorafenib inhibits growth and metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma by blocking STAT3. World J Gastroenterol 2011; 17(34): 3922-3932
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v17/i34/3922.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v17.i34.3922