Copyright
©2011 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Sep 14, 2011; 17(34): 3922-3932
Published online Sep 14, 2011. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v17.i34.3922
Published online Sep 14, 2011. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v17.i34.3922
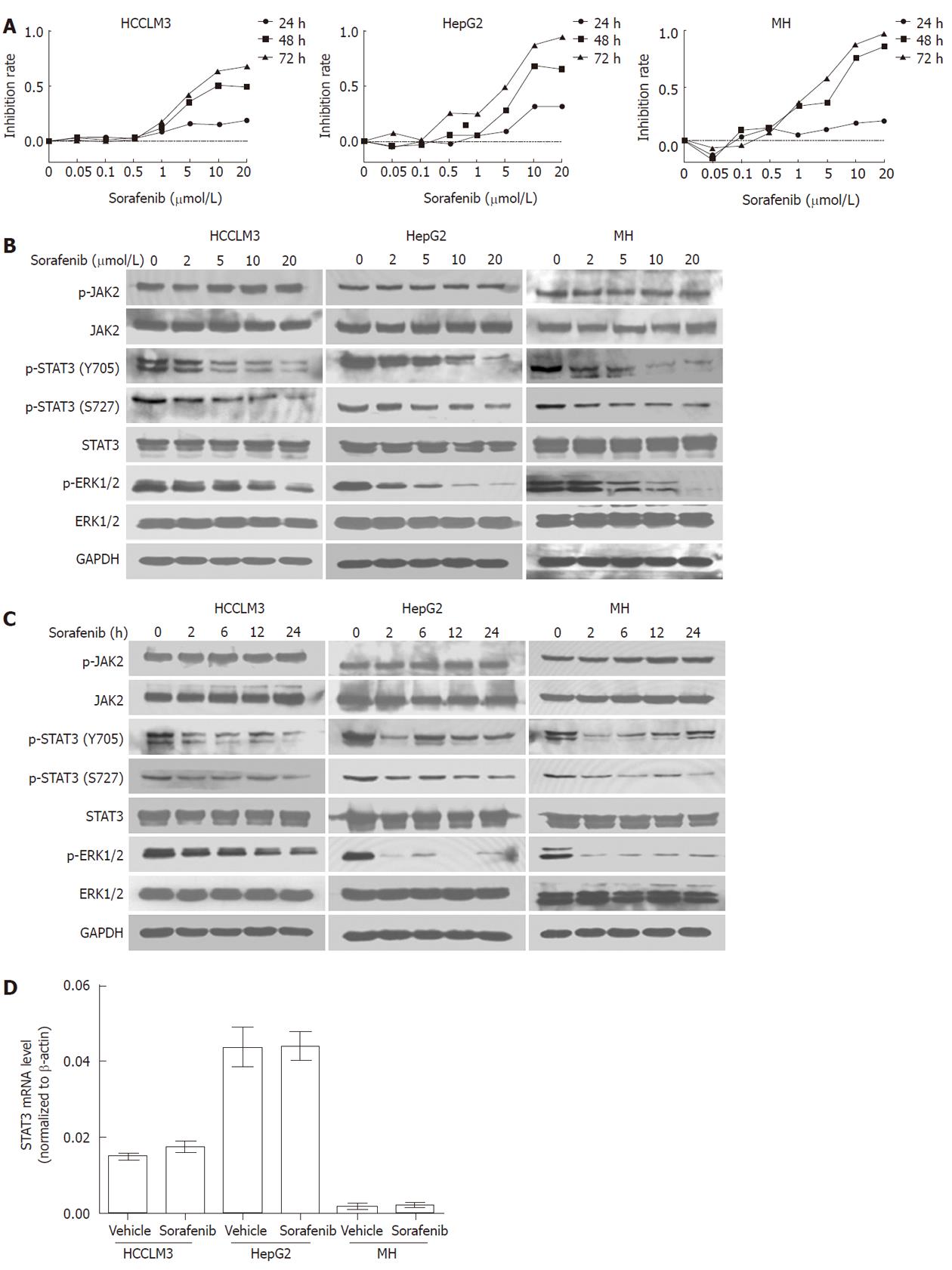
Figure 1 Inhibition of signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 signaling by sorafenib is associated with reduced cell proliferation.
A: Sorafenib inhibited cell proliferation in a time and dose-dependent manner, as assessed by the MTT assay; B: Sorafenib inhibited phosphorylation of signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3) and extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2, but not janus kinase 2 (JAK2), in a dose-dependent manner. Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) cells were exposed to sorafenib for 2 h, and proteins were analyzed by Western blot; C: Sorafenib durably inhibited phosphorylation of STAT3 and ERK1/2 but not JAK2. HCC cells were treated with 10 μmol/L sorafenib for different durations, and cell lysates were analyzed by Western blotting; D: Sorafenib did not affect STAT3 mRNA levels in HCC cell lines (P > 0.05 for all). After 24-h sorafenib treatment (10 μmol/L), STAT3 mRNA levels were analyzed by qRT-PCR.
- Citation: Gu FM, Li QL, Gao Q, Jiang JH, Huang XY, Pan JF, Fan J, Zhou J. Sorafenib inhibits growth and metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma by blocking STAT3. World J Gastroenterol 2011; 17(34): 3922-3932
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v17/i34/3922.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v17.i34.3922