Copyright
©2011 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Sep 14, 2011; 17(34): 3899-3911
Published online Sep 14, 2011. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v17.i34.3899
Published online Sep 14, 2011. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v17.i34.3899
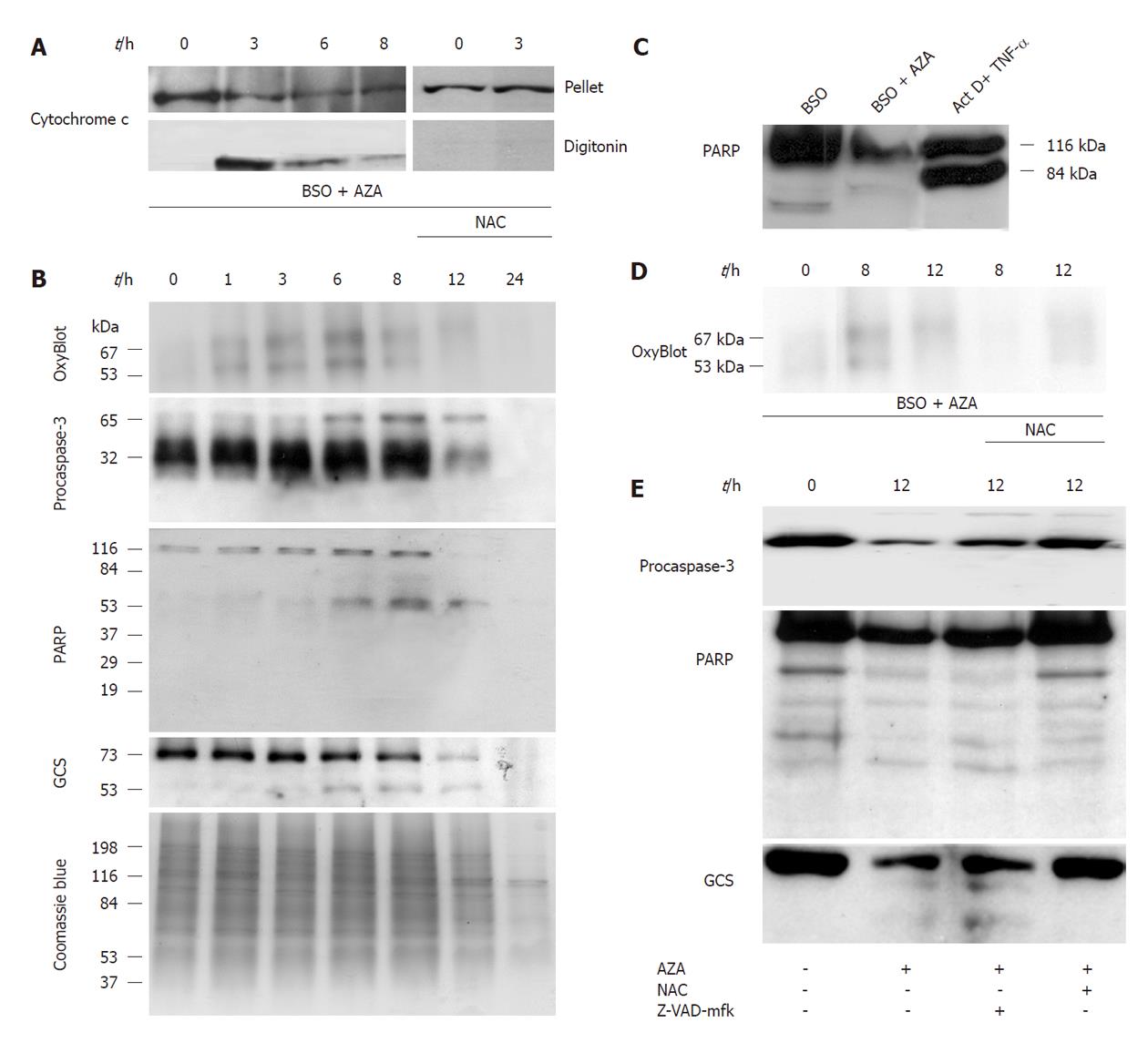
Figure 6 Effect of azathioprine plus buthionine sulfoximine treatment on biochemical markers of apoptosis.
A: Time course of cytochrome c release from HepG2 cells pretreated with buthionine sulfoximine (BSO) (500 μmol/L) during 24 h and then cotreated with azathioprine (AZA) (300 μmol/L) at different times. N-acetylcysteine (NAC) (1.5 mmol/L) was added at the same time as AZA; B: Time course of apoptosis-related proteins in HepG2 cells pretreated with BSO (500 μmol/L) for 24 h and then cotreated with AZA (300 μmol/L) at different times; C: Western blotting of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP) from HepG2 cells treated with BSO (500 μmol/L, 24 h) , or pretreated with BSO (500 μmol/L, 24 h) and then cotreated with AZA (300 μmol/L, 12 h). HepG2 cells treated with actinomycin D (0.8 μmol/L) plus tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α (35 pmol/L) for 18 h were used as positive control; D: Time course of the oxidized proteins from HepG2 cells treated in similar conditions as in panel A; E: Time course of apoptosis-related proteins from HepG2 cells treated in similar conditions as in panel A. NAC (1.5 mmol/L) or Z-VAD-mfk (50 μmol/L) were added at the same time as AZA. This set of experiments is representative of three others with similar results.
- Citation: Hernández-Breijo B, Monserrat J, Ramírez-Rubio S, Cuevas EP, Vara D, Díaz-Laviada I, Fernández-Moreno MD, Román ID, Gisbert JP, Guijarro LG. Preclinical evaluation of azathioprine plus buthionine sulfoximine in the treatment of human hepatocarcinoma and colon carcinoma. World J Gastroenterol 2011; 17(34): 3899-3911
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v17/i34/3899.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v17.i34.3899