Copyright
©2011 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Sep 7, 2011; 17(33): 3802-3809
Published online Sep 7, 2011. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v17.i33.3802
Published online Sep 7, 2011. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v17.i33.3802
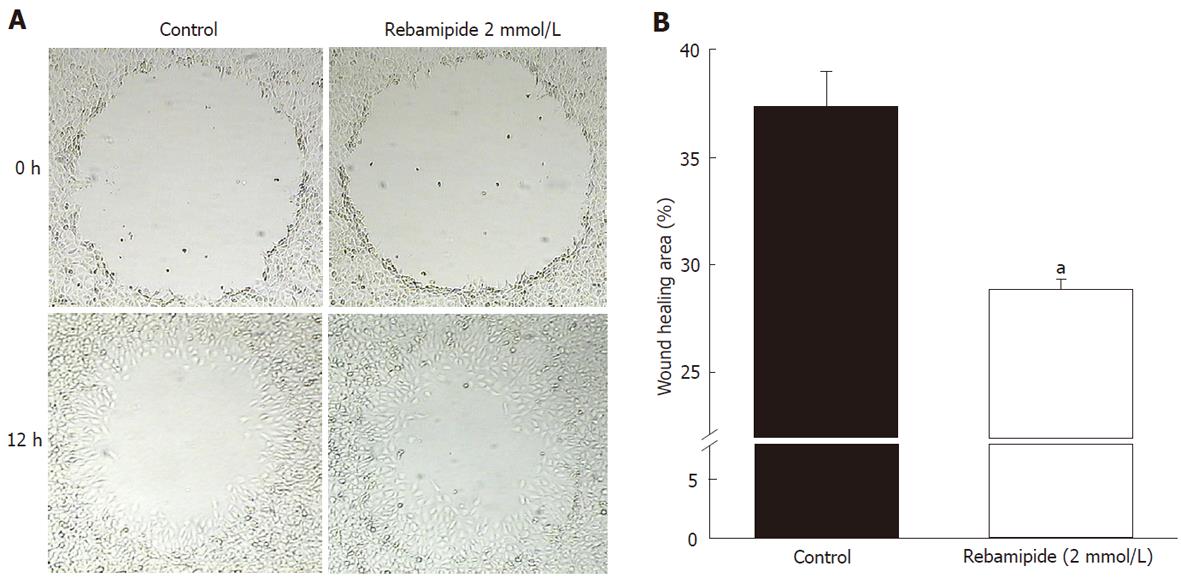
Figure 3 Restitution of rat intestinal epithelial cells around an artificially created wound in control and rebamipide-treated groups.
A: Restitution of rat intestinal epithelial (RIE) cells was evaluated using a wound assay. The denuded area of RIE cells recovered in a time-dependent manner after wound induction. Restitution of the denuded area was promoted by rebamipide at 12 h after wound induction. B: To investigate the effects of rebamipide on RIE cell migration, cells were co-incubated with 2 mmol/L rebamipide after wound induction. Wound repair in 2 mmol/L rebamipide-treated cells occurred significantly earlier than it did in the controls. Datas represent the mean ± SE of four experiments. aP < 0.05 vs controls.
- Citation: Takagi T, Naito Y, Uchiyama K, Okuda T, Mizushima K, Suzuki T, Handa O, Ishikawa T, Yagi N, Kokura S, Ichikawa H, Yoshikawa T. Rebamipide promotes healing of colonic ulceration through enhanced epithelial restitution. World J Gastroenterol 2011; 17(33): 3802-3809
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v17/i33/3802.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v17.i33.3802