Copyright
©2011 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Sep 7, 2011; 17(33): 3802-3809
Published online Sep 7, 2011. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v17.i33.3802
Published online Sep 7, 2011. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v17.i33.3802
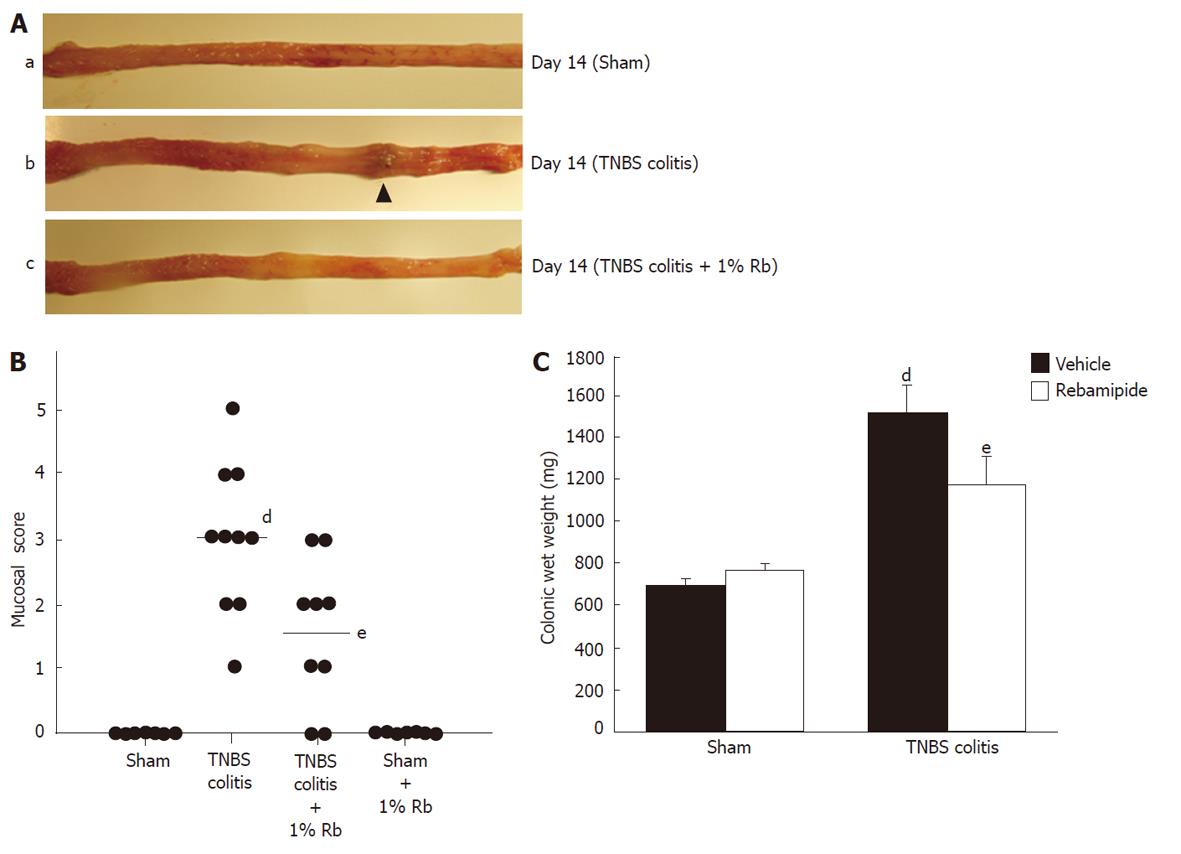
Figure 1 Effects of 1% rebamipide on macroscopic findings, mucosal damage score, and wet colon weight on day 14 after trinitrobenzene sulfonic acid-induced injury.
A: Severe colitis was induced with hyperemia, edema, thickening, ulceration, and necrosis in trinitrobenzene sulfonic acid (TNBS)-colitis rats (b) compared to sham-operated rats (a). These changes were reduced in rats treated with 1% rebamipide (TNBS-colitis rats treated with 1% rebamipide) (c). B: A 1% rebamipide enema was administrated twice daily starting on day 7 after induction of colitis, until day 14. Rats were sacrificed on day 14, and the mucosal damage score was evaluated. Data are expressed as a scatter plot. dP < 0.01 vs sham-treated rats. eP < 0.05 vs TNBS-induced colitis rats receiving the vehicle. C: Rats were sacrificed on day 14 and the distal colon was removed, after which, the wet colon weight was immediately measured. Data represent the mean ± SE of seven rats. dP < 0.01 vs sham-treated rats receiving the vehicle. eP < 0.01 vs TNBS-induced colitis rats receiving the vehicle.
- Citation: Takagi T, Naito Y, Uchiyama K, Okuda T, Mizushima K, Suzuki T, Handa O, Ishikawa T, Yagi N, Kokura S, Ichikawa H, Yoshikawa T. Rebamipide promotes healing of colonic ulceration through enhanced epithelial restitution. World J Gastroenterol 2011; 17(33): 3802-3809
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v17/i33/3802.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v17.i33.3802