Copyright
©2011 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Aug 28, 2011; 17(32): 3691-3699
Published online Aug 28, 2011. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v17.i32.3691
Published online Aug 28, 2011. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v17.i32.3691
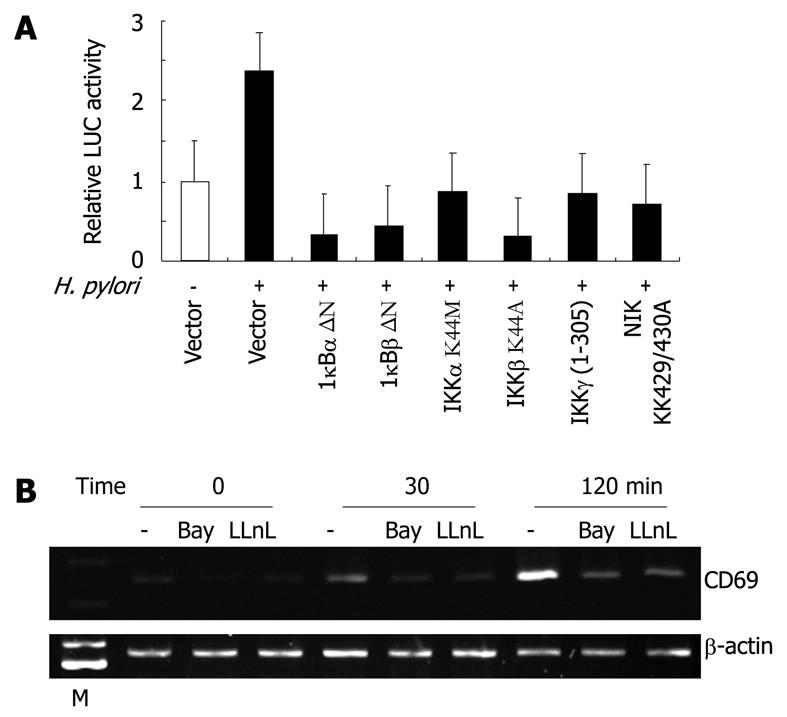
Figure 5 Nuclear factor-κB signal is essential for the activation of CD69 expression by Helicobacter pylori in T cells.
A: Functional effects of IκBα-, IκBβ-, and IKKγ-dominant-interfering mutants and kinase-deficient IKKα, IKKβ, and NIK mutants on Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori)-induced activation of the CD69 promoter. Jurkat cells were transfected with the CD69 reporter construct (pAIM-255-LUC) and the indicated mutant plasmids or empty vector (pCMV4) and then infected with H. pylori ATCC 49503 for 6 h. Open bar: Luciferase (LUC) activity of the CD69 reporter construct and pCMV4 without H. pylori infection. All values were calculated as the change (n-fold) in induction values relative to the basal level measured in uninfected cells. Data are mean ± SD of three independent experiments. B: Bay 11-7082 and N-acetyl-L-leucyl-L-leucyl-L-norleucinal (LLnL) inhibit CD69 mRNA expression induced by H. pylori. Jurkat cells were pretreated with Bay 11-7082 (20 μmol/L) or LLnL (20 μmol/L) for 2 h prior to H. pylori infection and subsequently infected with H. pylori ATCC 49503 for 30 or 120 min. CD69 mRNA expression on harvested cells was analyzed by reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction. Lane M: Markers.
-
Citation: Mori N, Ishikawa C, Senba M. Induction of CD69 expression by
cag PAI-positiveHelicobacter pylori infection. World J Gastroenterol 2011; 17(32): 3691-3699 - URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v17/i32/3691.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v17.i32.3691