Copyright
©2011 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Aug 28, 2011; 17(32): 3691-3699
Published online Aug 28, 2011. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v17.i32.3691
Published online Aug 28, 2011. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v17.i32.3691
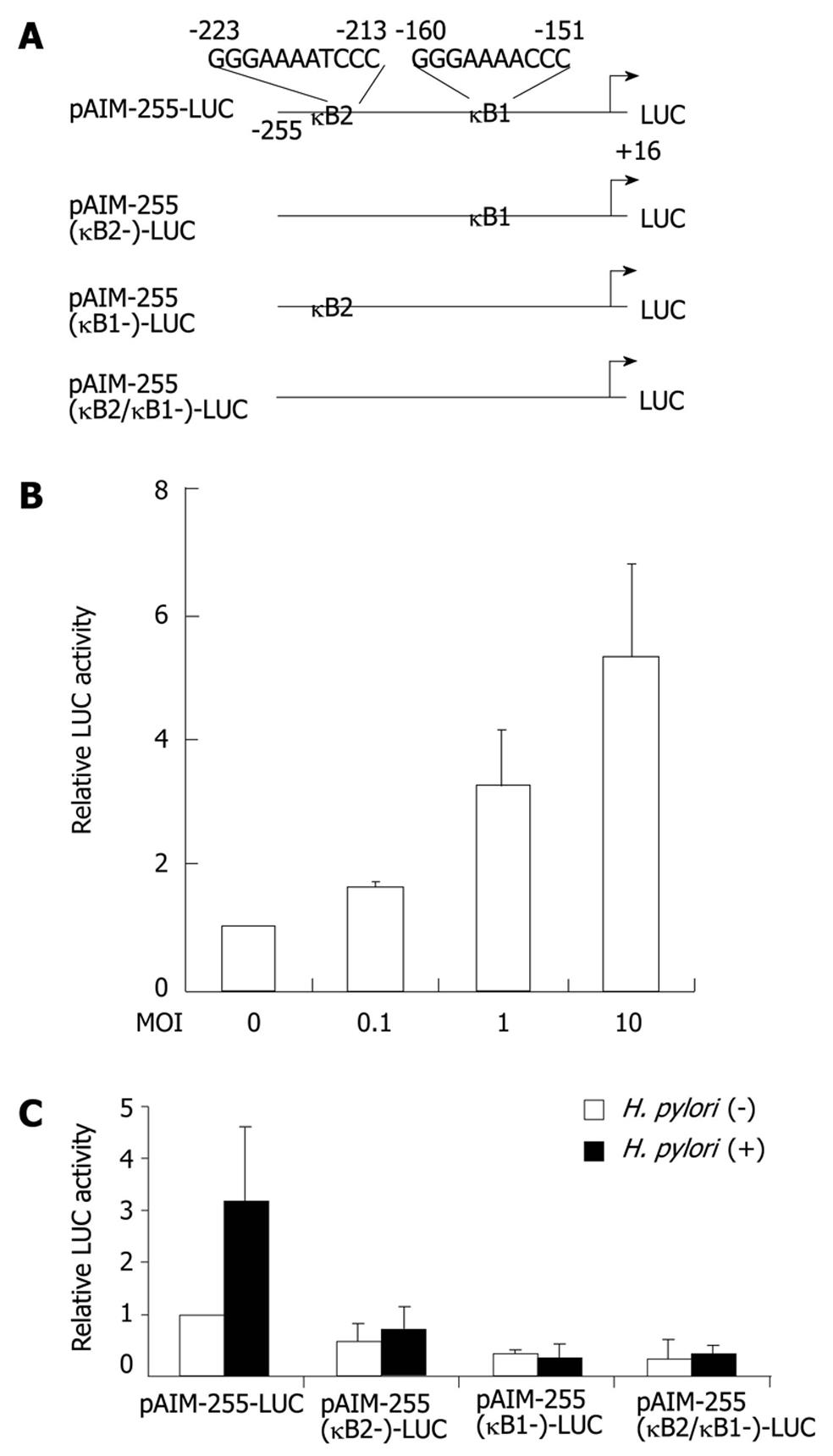
Figure 3 Helicobacter pylori activates the CD69 promoter through two nuclear factor-κB binding sites.
A: Schematic diagram of the CD69 reporter constructs containing the wild-type (pAIM-255-LUC) and internal deletion mutants of κB1 and/or κB2 motifs. LUC: Luciferase; B: Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) infection increases CD69 promoter activity in a dose-dependent fashion. pAIM-255-LUC was transfected into Jurkat cells, and the cells were subsequently infected with H. pylori ATCC 49503 for 6 h; C: The indicated CD69 reporter constructs were transfected into Jurkat cells, and subsequently the cells were infected with ATCC 49503 for 6 h (the multiplicity of infection of 10). The activity is expressed relative to that of cells transfected with pAIM-255-LUC without further H. pylori infection, which was defined as 1. Datas are mean ± SD of three experiments.
-
Citation: Mori N, Ishikawa C, Senba M. Induction of CD69 expression by
cag PAI-positiveHelicobacter pylori infection. World J Gastroenterol 2011; 17(32): 3691-3699 - URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v17/i32/3691.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v17.i32.3691