Copyright
©2011 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Aug 28, 2011; 17(32): 3691-3699
Published online Aug 28, 2011. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v17.i32.3691
Published online Aug 28, 2011. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v17.i32.3691
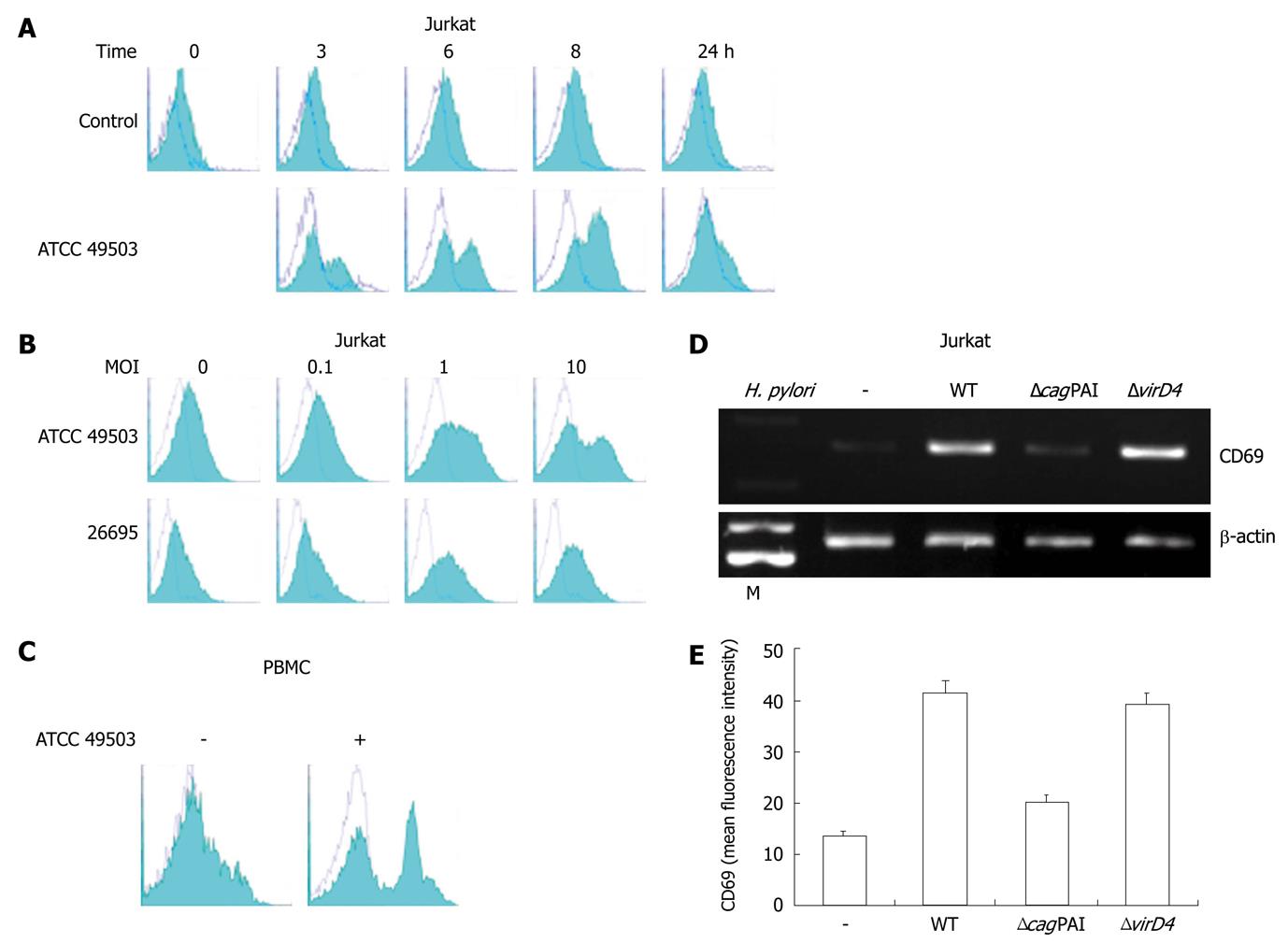
Figure 2 CD69 expression on Jurkat cells.
A: Time course of cell surface expression of CD69 on Jurkat cells exposed to Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori). Jurkat cells were cultured for the indicated times in culture medium (control) or in the presence of ATCC 49503 [the multiplicity of infection (MOI) of 10]. After cell harvest, CD69 expression on the cells was determined by flow cytometry; B: H. pylori infection increases cell surface expression of CD69 on Jurkat cells in a dose-dependent fashion. Jurkat cells were infected with different concentrations of H. pylori strains, ATCC 49503 and 26695, and CD69 levels were measured by flow cytometry on cells harvested after 8 h; C: H. pylori infection increases cell surface expression of CD69 on peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs). PBMCs were infected with ATCC 49503 (MOI of 10), and CD69 levels were measured on cells harvested after 8 h; D: cag pathogenicity island (cagPAI) products of H. pylori are required for the induction of CD69 mRNA expression. Total RNA was extracted from Jurkat cells that had been infected with the wild-type strain 26695 (WT) or the isogenic mutants ΔcagPAI and ΔvirD4 (MOI of 10) for 2 h and used for reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction. Lane M: Markers; E: Flow cytometric analysis was carried out for the surface expression of CD69 in Jurkat cells infected with the wild-type strain 26695 (WT) or the isogenic mutants ΔcagPAI and ΔvirD4. Jurkat cells were infected for 8 h with various H. pylori strains (MOI of 10). Cells were stained with phycoerythrin-labeled monoclonal antibody. Datas are mean ± SD of three experiments.
-
Citation: Mori N, Ishikawa C, Senba M. Induction of CD69 expression by
cag PAI-positiveHelicobacter pylori infection. World J Gastroenterol 2011; 17(32): 3691-3699 - URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v17/i32/3691.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v17.i32.3691