Copyright
©2011 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Aug 28, 2011; 17(32): 3691-3699
Published online Aug 28, 2011. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v17.i32.3691
Published online Aug 28, 2011. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v17.i32.3691
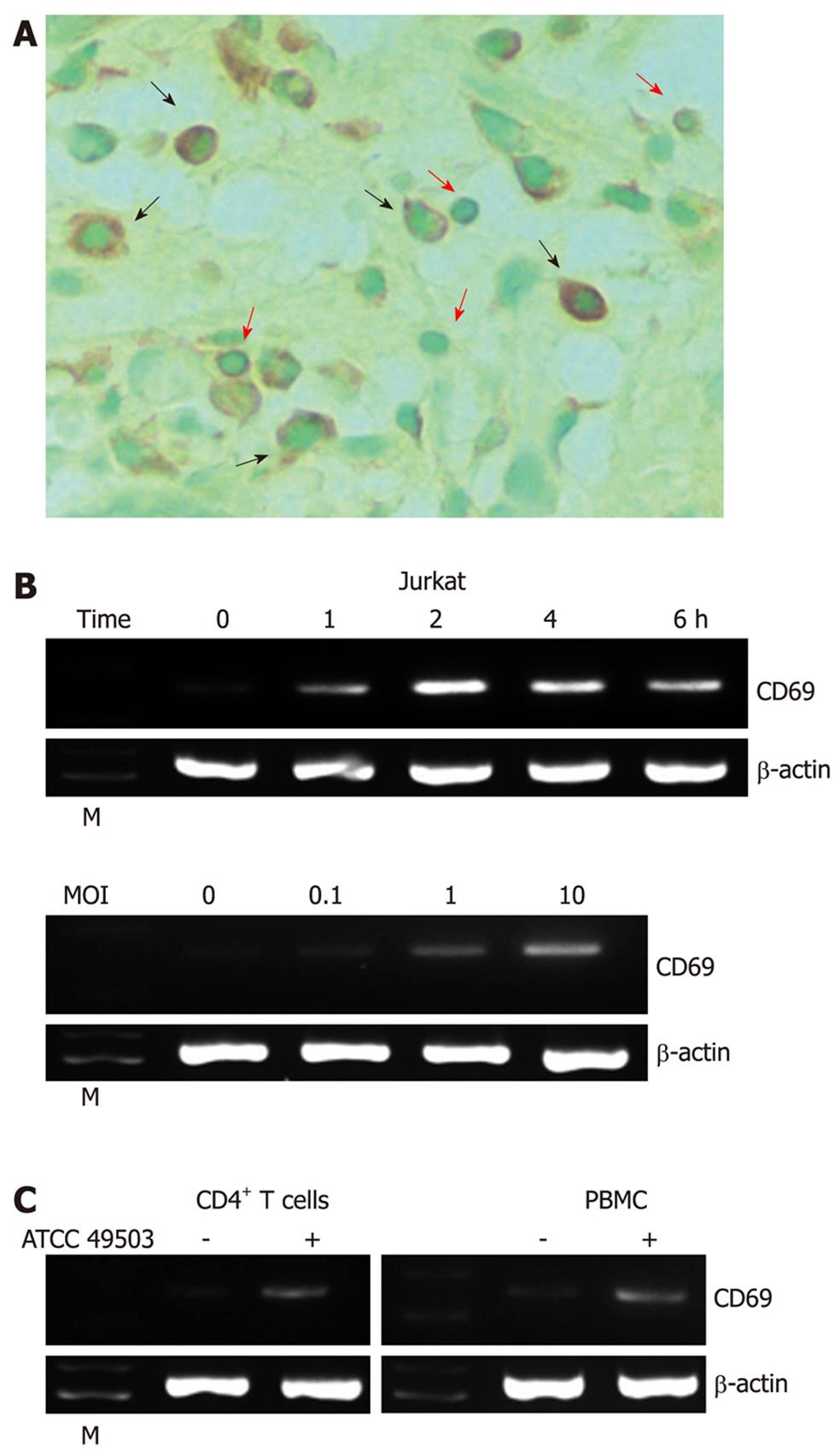
Figure 1 Expression of CD69 in Helicobacter pylori-infected T cells.
A: Immunohistochemical detection of CD69 in tissues of patients with Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori)-positive gastritis. Serial sections of gastric biopsy specimens were stained with a mouse monoclonal antibody to CD69 and counterstained with methyl green. Shown is a representative example of mucosa from a patient with H. pylori-positive gastritis. Note the positive staining for CD69 in lymphocytes as well as macrophages. Original magnification, × 800. The red and black arrows indicate the surfaces of lymphocytes and macrophages, respectively; B: H. pylori-induced CD69 mRNA expression in Jurkat cells. Total RNA was extracted from Jurkat cells infected with H. pylori strain ATCC 49503 [the multiplicity of infection (MOI) of 100] for the indicated time intervals and used for reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) (top). Jurkat cells were infected with the indicated concentrations of ATCC 49503 for 2 h. Total RNA was extracted and used for RT-PCR (bottom); C: H. pylori-induced CD69 mRNA expression in peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) and CD4+ T cells. Total RNA was extracted from PBMCs and CD4+ T cells infected with ATCC 49503 for 2 h and used for RT-PCR (MOI of 10). β-actin expression served as a control. Lane M: Markers.
-
Citation: Mori N, Ishikawa C, Senba M. Induction of CD69 expression by
cag PAI-positiveHelicobacter pylori infection. World J Gastroenterol 2011; 17(32): 3691-3699 - URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v17/i32/3691.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v17.i32.3691