Copyright
©2011 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Aug 21, 2011; 17(31): 3605-3613
Published online Aug 21, 2011. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v17.i31.3605
Published online Aug 21, 2011. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v17.i31.3605
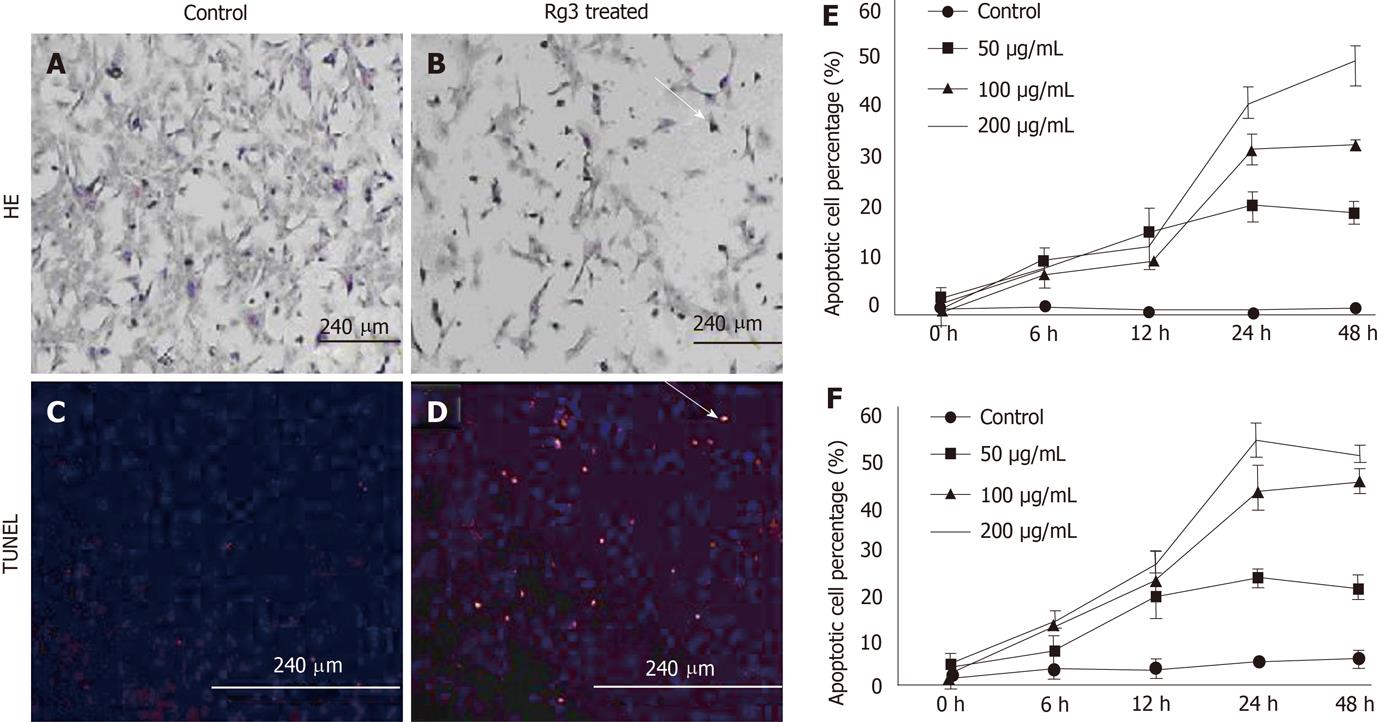
Figure 2 Ginsenoside Rg3 caused hepatocellular carcinoma morphological changes of apoptotic cells.
A, B: Cell apoptosis morphology was observed by hematoxylin and eosin (HE) stain. After 50 μg/mL Ginsenoside Rg3 (Rg3) incubation for 12 h, the Hep1-6 cells (B) indicate less survival cells compared to control group (A); C, D: DNA fragmentation in situ was detected by transferase-mediated dUTP-biotin nick end labeling. The control cells was stained blue (C) and the Rg3 treated group present apoptotic cells stained red (D); E, F: The apoptotic cells showed reduced volume and condensed chromatin. In both Hep1-6 and HepG2, the apoptotic induction effect is dose and time-dependent. Rg3: Ginsenoside Rg3; HE: Hematoxylin and eosin; TUNEL: Transferase-mediated dUTP-biotin nick end labeling.
-
Citation: Jiang JW, Chen XM, Chen XH, Zheng SS. Ginsenoside Rg3 inhibit hepatocellular carcinoma growth
via intrinsic apoptotic pathway. World J Gastroenterol 2011; 17(31): 3605-3613 - URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v17/i31/3605.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v17.i31.3605