Copyright
©2011 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Jan 21, 2011; 17(3): 300-312
Published online Jan 21, 2011. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v17.i3.300
Published online Jan 21, 2011. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v17.i3.300
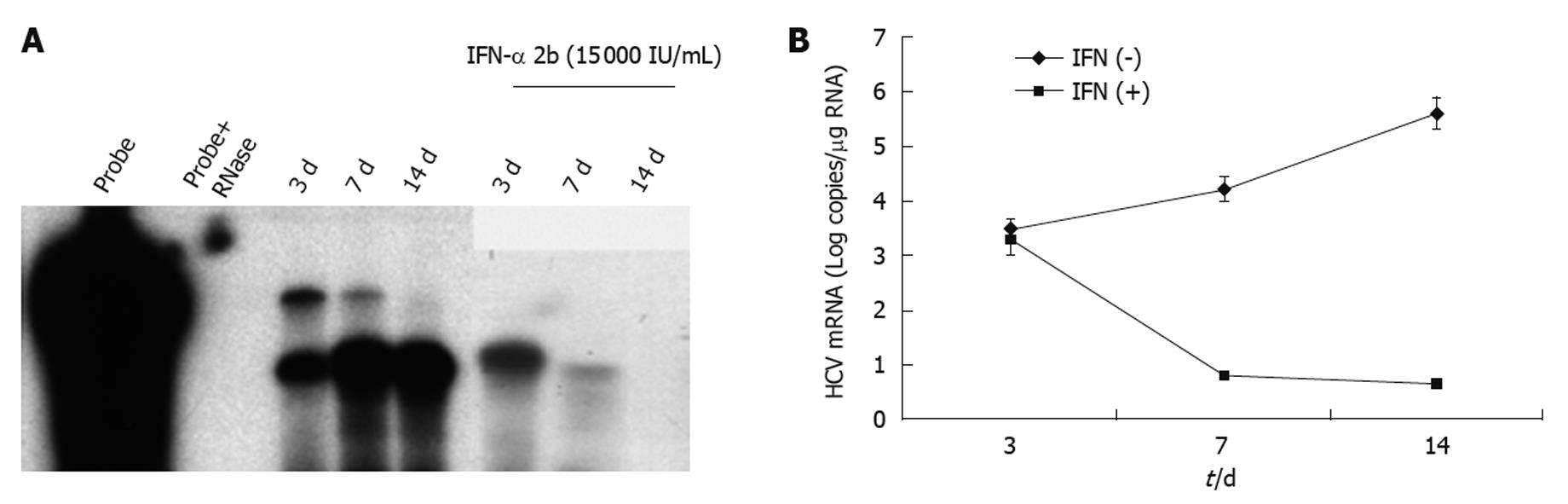
Figure 6 Intracellular hepatitis C virus RNA levels in subcutaneous tumors.
A: RPA measuring intracellular hepatitis C virus (HCV) RNA levels in hepatocellular xenografts formed subcutaneously. There was a gradual increase in HCV RNA levels in the subcutaneous tumors at 3, 7 and 14 d post-tumor development. Two weeks of interferon (IFN) treatment completely inhibited HCV RNA replication in the subcutaneous tumors, as demonstrated by a negative RPA signal at 14 d of IFN-α treatment; B: Real-time reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction showing HCV RNA levels in the subcutaneous tumors before and after IFN-α treatment. IFN treatment decreased HCV RNA levels in the tumors, which remained below the detection limits after 2 wk.
- Citation: Hazari S, Hefler HJ, Chandra PK, Poat B, Gunduz F, Ooms T, Wu T, Balart LA, Dash S. Hepatocellular carcinoma xenograft supports HCV replication: A mouse model for evaluating antivirals. World J Gastroenterol 2011; 17(3): 300-312
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v17/i3/300.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v17.i3.300