Copyright
©2011 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Jul 28, 2011; 17(28): 3310-3321
Published online Jul 28, 2011. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v17.i28.3310
Published online Jul 28, 2011. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v17.i28.3310
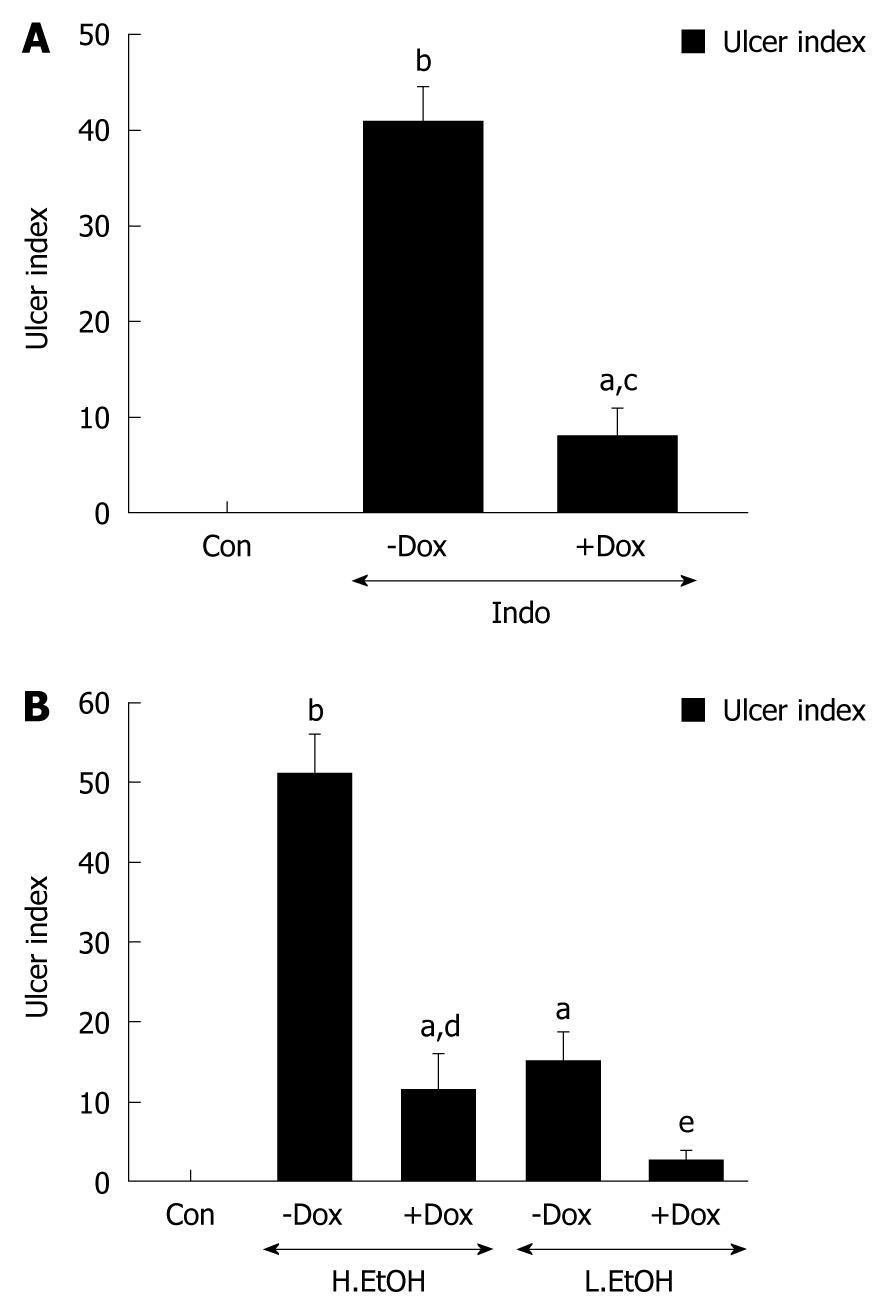
Figure 1 Protective effect of doxycycline on gastric injury.
Gastric ulcers were induced in rats by oral administration of 48 mg/kg indomethacin or 70% ethanol (low and high) doses. Doxycycline (50 mg/kg) was administered orally prior to ulcerogen treatment to assess the protective effect. Control rats received sterile water only. After 3 h, rats were sacrificed and ulcer indices were scored. Mean ulcer index for indomethacin-induced (A) and ethanol-induced (B) ulceration in each group of rats was plotted. Dox: Doxycycline; Con: Control; Indo: Indomethacin; L.EtOH: Low dose ethanol; H.EtOH: High dose ethanol. Data expressed as mean ± SE. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.001 vs control; cP < 0.001 vs indomethacin; dP < 0.001 vs high dose ethanol; eP < 0.01 vs low dose ethanol.
- Citation: Singh LP, Mishra A, Saha D, Swarnakar S. Doxycycline blocks gastric ulcer by regulating matrix metalloproteinase-2 activity and oxidative stress. World J Gastroenterol 2011; 17(28): 3310-3321
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v17/i28/3310.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v17.i28.3310