Copyright
©2011 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Jul 28, 2011; 17(28): 3300-3309
Published online Jul 28, 2011. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v17.i28.3300
Published online Jul 28, 2011. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v17.i28.3300
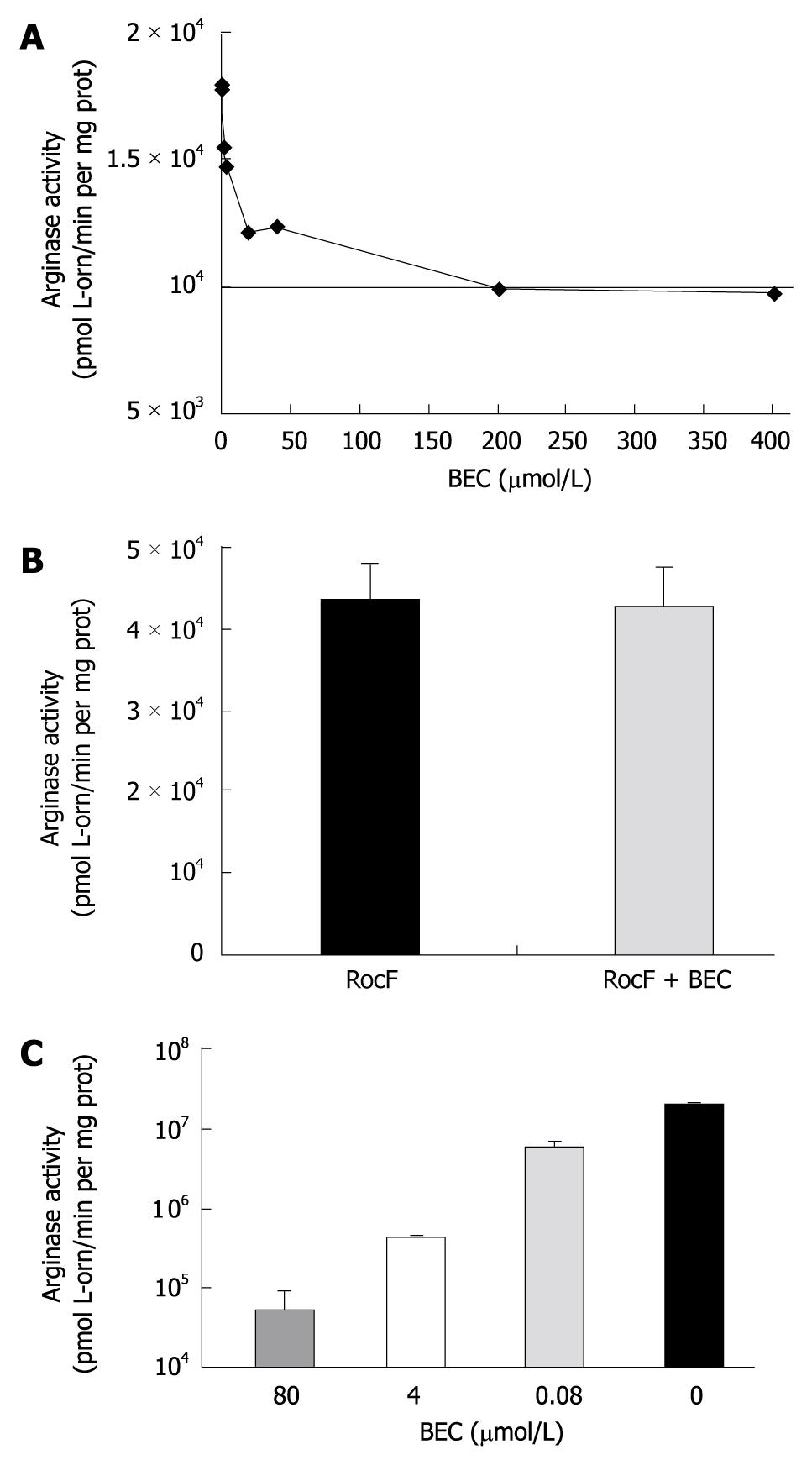
Figure 6 S-(2-boronoethyl)-L-cysteine does not strongly inhibit Helicobacter pylori arginase activity in vitro.
A: Arginase-containing extracts from Escherichia coli (E. coli) expressing the Helicobacter pylori rocF gene on pGEN222. Extracts were incubated in the presence or absence of various concentrations of S-(2-boronoethyl)-L-cysteine (BEC) and measured for arginase activity at pH 6.0 in the presence of cobalt; B: Purified arginase (His6-RocF) was incubated in the presence or absence of BEC (400 nmol/L) and assayed for arginase activity in the presence of cobalt at pH 6.0; C: Extracts from E. coli expressing rat arginase I were prepared and incubated in the presence of different concentrations of BEC and then assayed for arginase activity in the presence of manganese at pH 9.0. Graph plotted on a logarithmic scale due to magnitude of arginase activity.
-
Citation: Kim SH, Langford ML, Boucher JL, Testerman TL, McGee DJ.
Helicobacter pylori arginase mutant colonizes arginase II knockout mice. World J Gastroenterol 2011; 17(28): 3300-3309 - URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v17/i28/3300.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v17.i28.3300