Copyright
©2011 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Jun 28, 2011; 17(24): 2879-2889
Published online Jun 28, 2011. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v17.i24.2879
Published online Jun 28, 2011. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v17.i24.2879
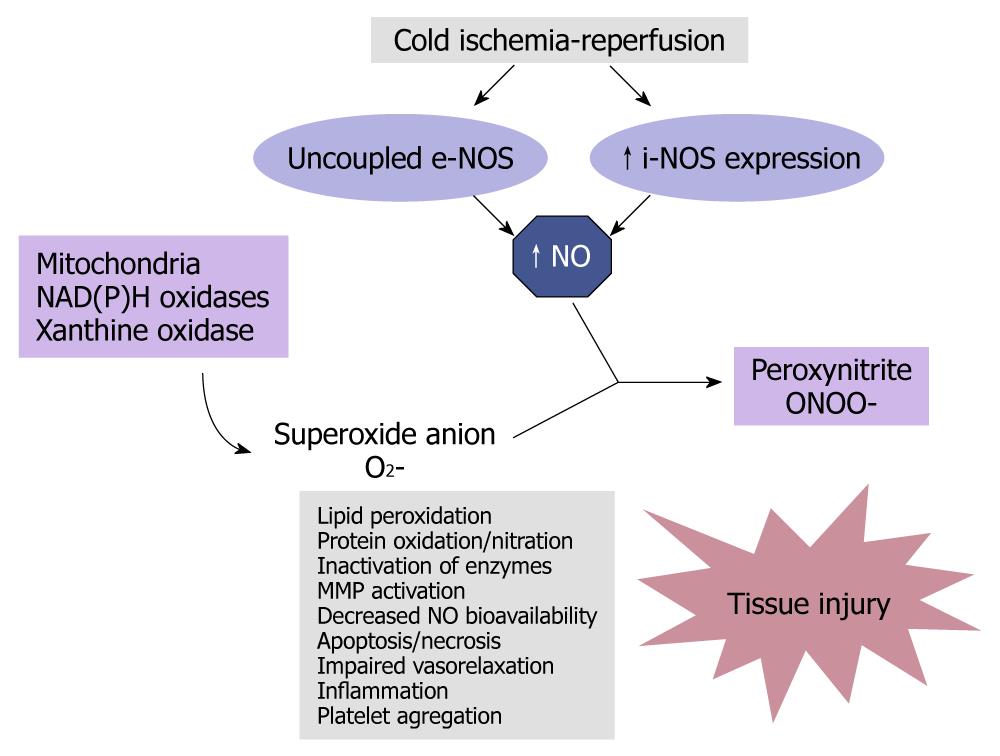
Figure 3 Tissue damage after unbalanced nitric oxide production.
Cold ischemia reperfusion involves uncoupled endothelial nitric oxide synthase (e-NOS) and inducible nitric oxide synthase (i-NOS) expression. Large amounts of nitric oxide (NO) are produced under these pathological conditions. NO, in association with increased mitochondrial dysfunction and oxidative stress, reacts with superoxide anion (O2-), to produce peroxynitrite (ONOO-). Peroxynitrite, in concert with other oxidants, induces tissue damage.
- Citation: Abdennebi HB, Zaoualí MA, Alfany-Fernandez I, Tabka D, Roselló-Catafau J. How to protect liver graft with nitric oxide. World J Gastroenterol 2011; 17(24): 2879-2889
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v17/i24/2879.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v17.i24.2879