Copyright
©2011 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Jun 21, 2011; 17(23): 2801-2811
Published online Jun 21, 2011. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v17.i23.2801
Published online Jun 21, 2011. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v17.i23.2801
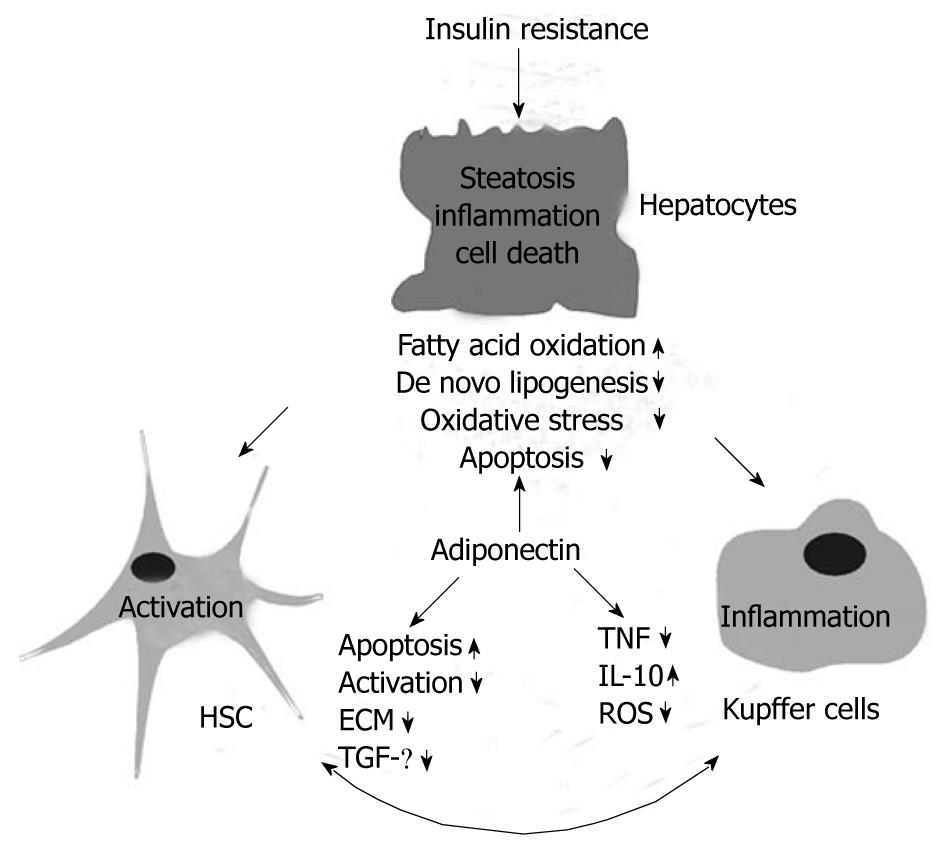
Figure 3 Hepatoprotective effects of adiponectin.
Hepatic insulin resistance correlates with liver fat content, and is currently thought to represent the first incident in metabolic liver diseases. Insulin resistance and steatosis may also promote inflammation and fibrosis although the factors leading to advanced liver damage have not been identified so far. Major pathophysiological alterations of hepatocytes, hepatic stellate cells (HSC) and Kupffer cells in hepatic steatosis and/or non-alcoholic steatohepatitis are indicated. The protective activities of adiponectin are listed and arrows indicate an induction or repression of these pathways/proteins by adiponectin. IL: Interleukin; TGF: Transforming growth factor; TNF: Tumor necrosis factor; ECM: extracellular matrix; ROS: Reactive oxygen species.
- Citation: Buechler C, Wanninger J, Neumeier M. Adiponectin, a key adipokine in obesity related liver diseases. World J Gastroenterol 2011; 17(23): 2801-2811
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v17/i23/2801.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v17.i23.2801