Copyright
©2011 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. May 28, 2011; 17(20): 2482-2499
Published online May 28, 2011. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v17.i20.2482
Published online May 28, 2011. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v17.i20.2482
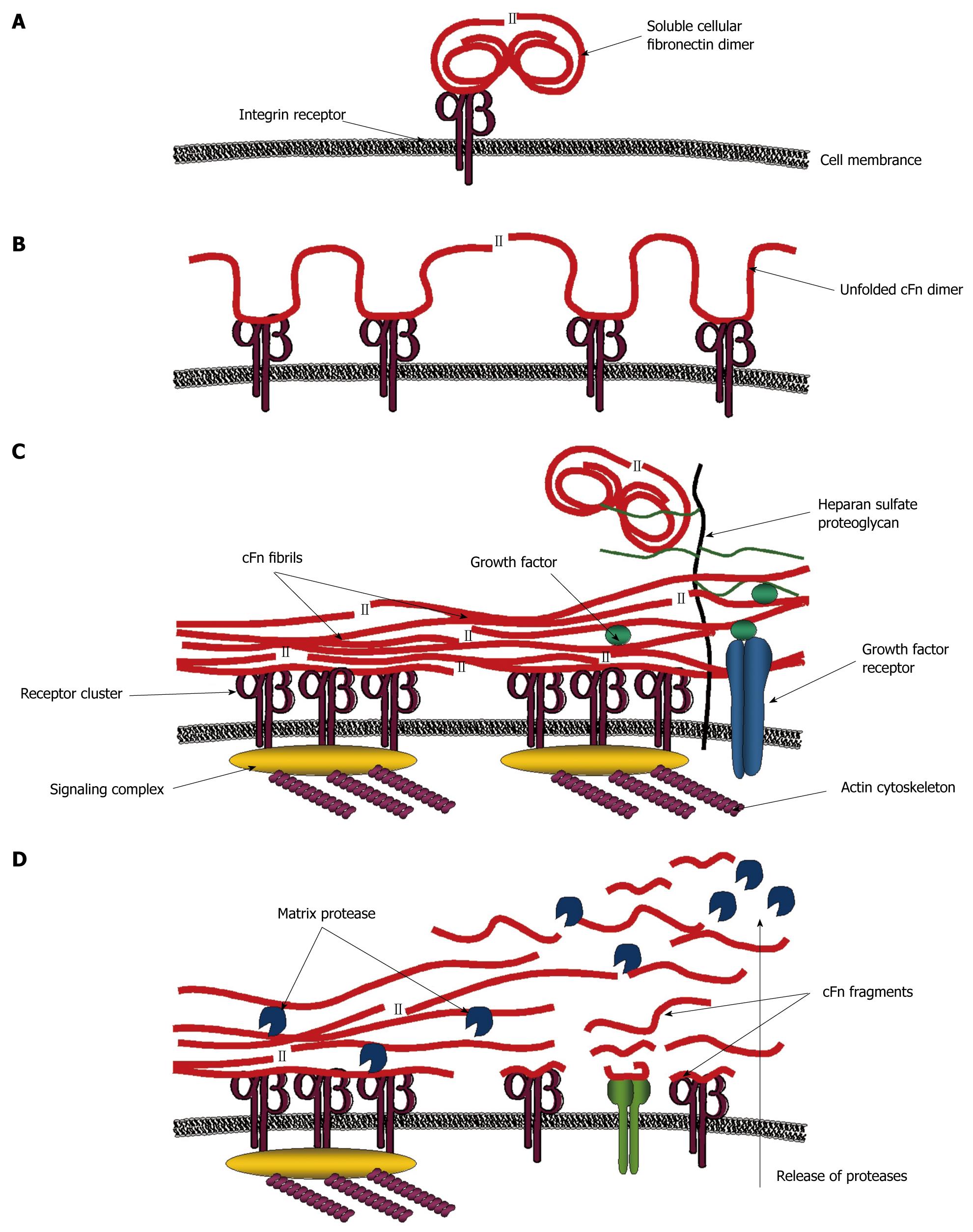
Figure 2 Model for signaling processes mediated by fibronectin.
A: Initial signals are mediated when soluble compact cellular fibronectin (cFn) binds a cognate receptor; B: This causes cFn to unfold and interact with other receptors inducing further signals; C: Receptor clustering and the formation of signaling complexes lead to the reorganization of the actin cytoskeleton which creates tensile forces, conveyed through the integrin receptors to further stretch cFn into fibrillar form. Exposed cryptic sites interact with other cFn fibrils in matrix assembly. Access to growth factors and other molecules is regulated by cFn binding. Heparan sulfate proteoglycans also bind to cFn and recruit distant molecules closer to the cell surface; D: All of these interactions create a cascade of different signals, some of which promote matrix protease release. Resulting cFn fragments activate additional intracellular signaling pathways. Thus, cFn can regulate cell behavior via numerous different mechanisms.
- Citation: Aziz-Seible RS, Casey CA. Fibronectin: Functional character and role in alcoholic liver disease. World J Gastroenterol 2011; 17(20): 2482-2499
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v17/i20/2482.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v17.i20.2482