Copyright
©2011 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Jan 14, 2011; 17(2): 164-173
Published online Jan 14, 2011. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v17.i2.164
Published online Jan 14, 2011. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v17.i2.164
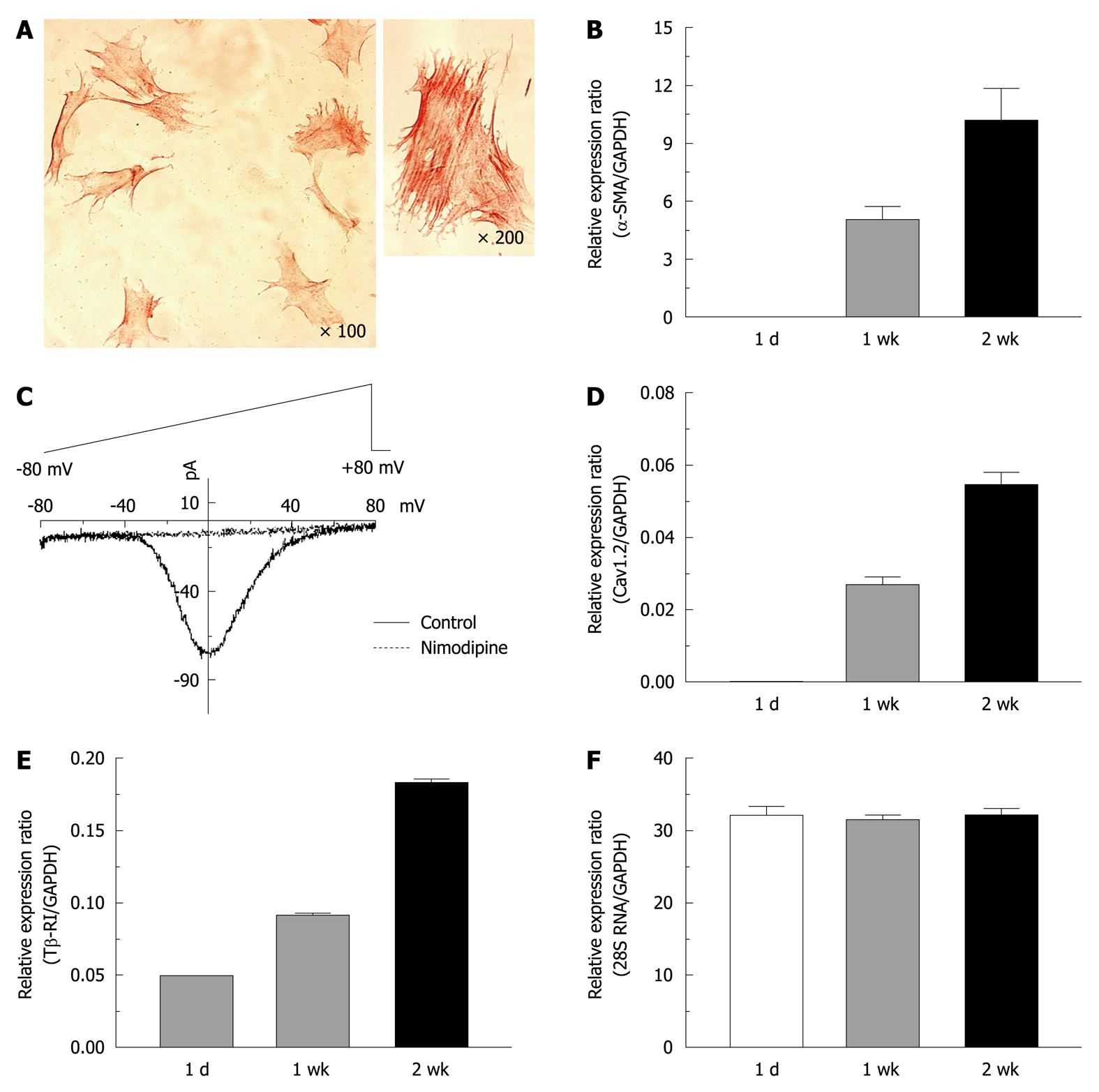
Figure 1 Expression of α-smooth muscle actin, L-type calcium channels and type 1 transforming growth factor-β receptors in activated rat hepatic stellate cells.
A: Immunocytochemical staining for α-smooth muscle actin (α-SMA) was performed on hepatic stellate cells (HSCs) cultured for 1 wk; C: Whole cell Ca2+ currents in a voltage-clamp mode were recorded from 2 wk-cultured HSCs, and were completely blocked by nimodipine (10 μmol/L); Changes in the transcript levels of α-SMA (B), the α1c subunit of the L-type Ca2+ channel (Cav1.2) (D), the type 1 receptor of transforming growth factor-β (Tβ-RI) (E), and 28S RNA (F) during HSC culturing (1 d, 1 wk and 2 wk) were measured by quantitative real-time reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction analysis. Expression levels were normalized to glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH) and expressed as a relative expression ratio (target/GAPDH). Data are presented as the mean ± SE (n = 3).
- Citation: Park KS, Sin PJ, Lee DH, Cha SK, Kim MJ, Kim NH, Baik SK, Jeong SW, Kong ID. Switching-on of serotonergic calcium signaling in activated hepatic stellate cells. World J Gastroenterol 2011; 17(2): 164-173
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v17/i2/164.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v17.i2.164