Copyright
©2011 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Jan 14, 2011; 17(2): 151-163
Published online Jan 14, 2011. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v17.i2.151
Published online Jan 14, 2011. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v17.i2.151
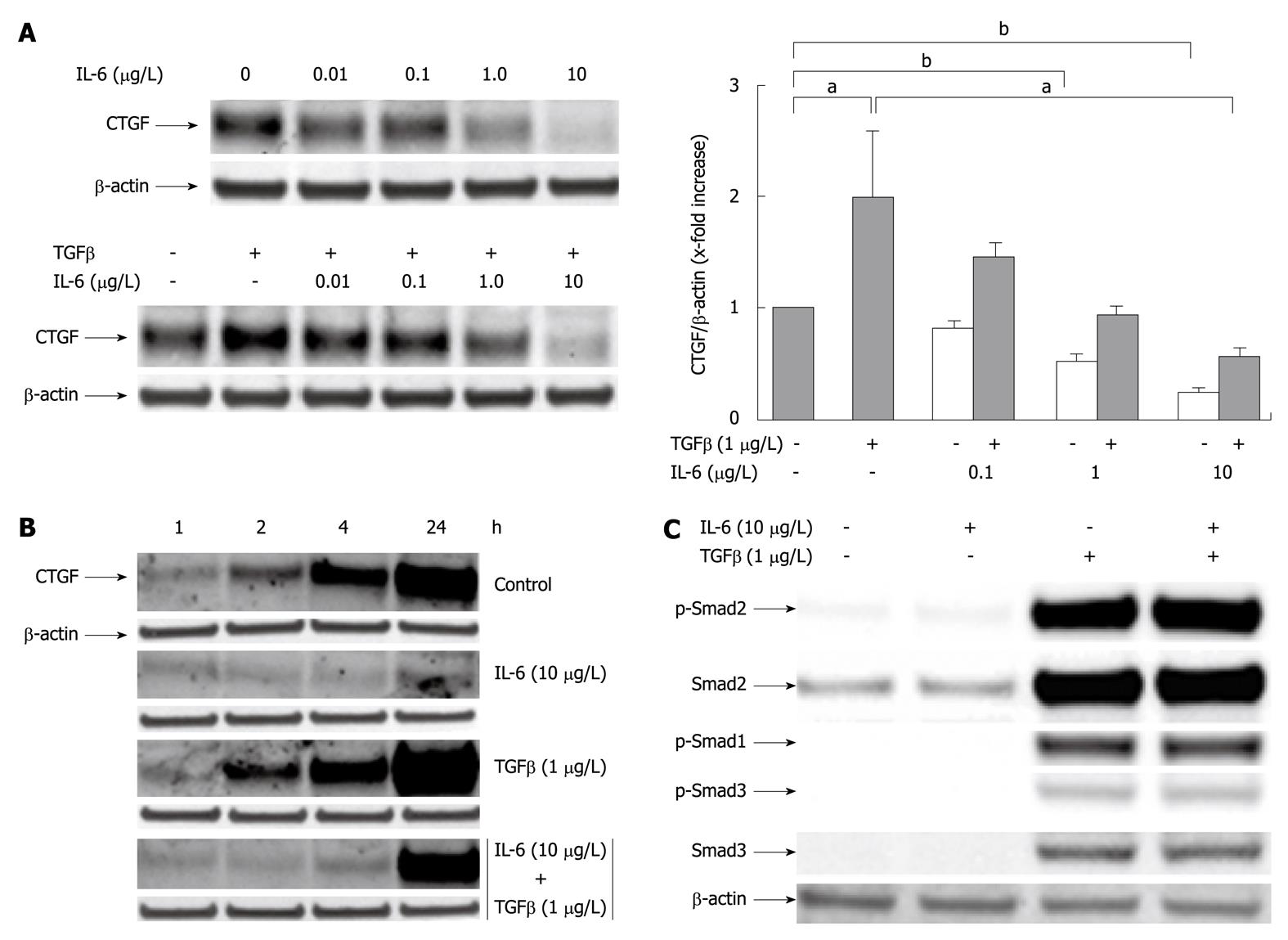
Figure 2 Interleukin-6 acts as an inhibitor of transforming growth factor β1 induced CYR61/CTGF/NOV 2/connective tissue growth factor protein expression in cultured rat hepatocytes.
A: Western blottings of CYR61/CTGF/NOV (CCN) 2/connective tissue growth factor (CTGF) of rat hepatocytes (PC) cultured under serum-free conditions with or without addition of rr interleukin (rrIL)-6 at indicated concentrations 30 min prior addition of rhTGFβ1 (1 μg/L). The cell culture only with IL-6 at indicated concentrations served as internal control. Cells were harvested after another 24 h. β-actin served as loading control. Representative blots are shown. Blots were quantified relative to β-actin using the Lumi Imager System. Quantifications represent the mean ± SD of 3 independent cultures. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.0001 vs untreated control; B: Western blottings of CCN2/CTGF of rat PC cultured as stated in (A) under serum-free conditions with or without addition of rrIL-6 (10 μg/L) 30 min prior addition of rhTGFβ1 (1 μg/L) where indicated. The cells were harvested after 1, 2, 4 and 24 h. β-actin served as loading control. A representative blot of 3 independent experiments is shown; C: Western blottings of phosphorylated and total Smad2 and Smad3, the latter antibody cross-reacting with Smad1. Rat PC were cultured for 24 h under serum-free conditions with or without addition of rh transforming growth factor (TGF) β1 (1 μg/L) and indicated concentrations of rrIL-6. Representative blots are shown.
- Citation: Gressner OA, Peredniene I, Gressner AM. Connective tissue growth factor reacts as an IL-6/STAT3-regulated hepatic negative acute phase protein. World J Gastroenterol 2011; 17(2): 151-163
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v17/i2/151.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v17.i2.151