Copyright
©2011 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. May 14, 2011; 17(18): 2315-2325
Published online May 14, 2011. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v17.i18.2315
Published online May 14, 2011. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v17.i18.2315
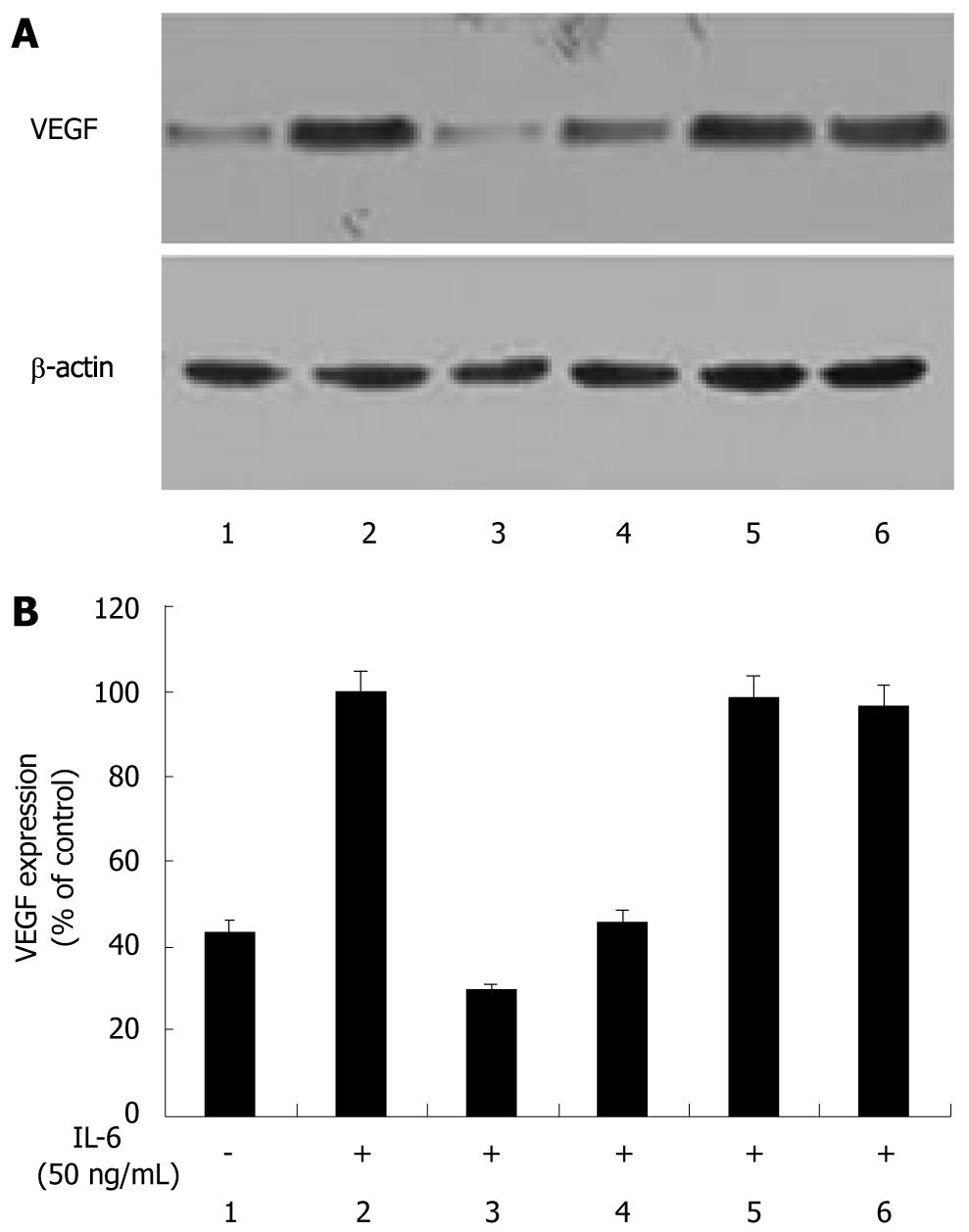
Figure 2 (-)-Epigallocatechin-3-gallate inhibits interleukin-6-induced vascular endothelial growth factor expression in human gastric cancer cells via JAK/STAT pathway.
Human gastric cancer (AGS) cells were stimulated with interleukin-6 (IL-6) (50 ng/mL) for 24 h in the presence of 50 μmol (-)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG) or signaling inhibitors. Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) protein levels in tumor cell lysates were analyzed by Western blotting. IL-6 markedly increased VEGF expression in AGS cells. When treated with EGCG or AG490, VEGF expression was significantly reduced. PD98059 and LY294002 did not change IL-6-induced VEGF expression. 1: Without IL-6 stimulation; 2: Stimulated with IL-6; 3-6: Treated with 50 μmol EGCG or signaling inhibitors of 20 μmol AG490, 25 μmol PD98059 or 25 μmol LY294002.
-
Citation: Zhu BH, Chen HY, Zhan WH, Wang CY, Cai SR, Wang Z, Zhang CH, He YL. (-)-Epigallocatechin-3-gallate inhibits VEGF expression induced by IL-6
via Stat3 in gastric cancer. World J Gastroenterol 2011; 17(18): 2315-2325 - URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v17/i18/2315.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v17.i18.2315