Copyright
©2011 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. May 7, 2011; 17(17): 2199-2205
Published online May 7, 2011. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v17.i17.2199
Published online May 7, 2011. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v17.i17.2199
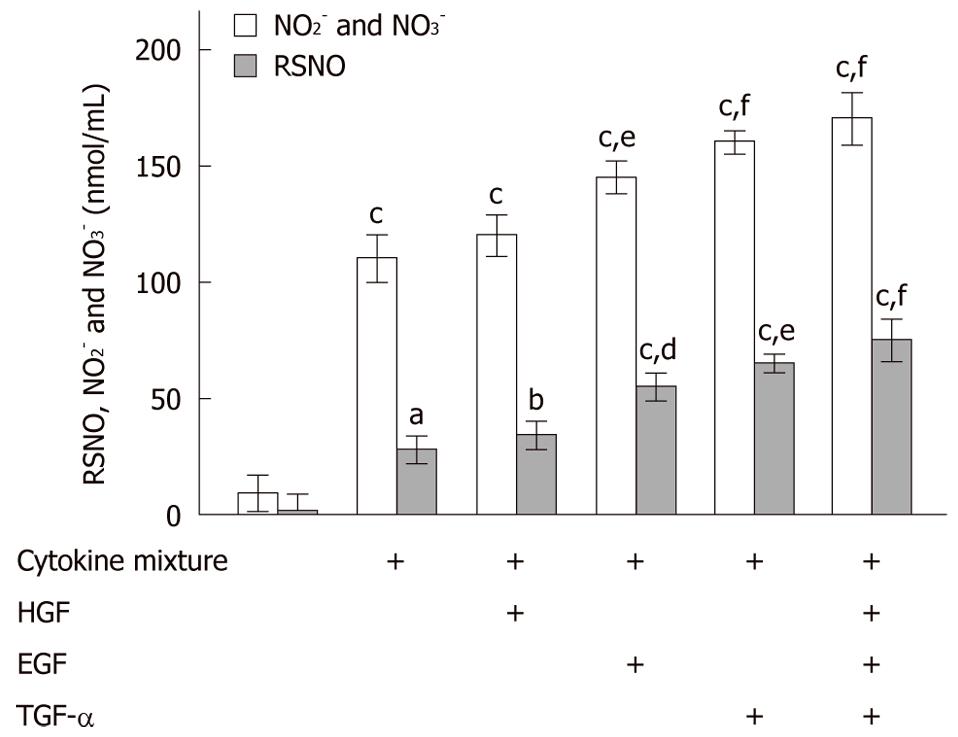
Figure 3 Hepatotropic growth factors increase nitric oxide formation in primary rat hepatocytes.
NO2- plus NO3- (empty bars) and RSNO (grey bars) levels demonstrated a significant increase after hepatocyte (N = 5, n = 3) pretreatment with growth factors and subsequent stimulation with lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-containing cytokine mixture (CM), if compared to treatment with LPS-containing CM alone [except for pretreatment with hepatocyte growth factor (HGF) alone]. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.005, cP < 0.001 vs corresponding untreated rat hepatocytes; dP < 0.05, eP < 0.005, fP < 0.001 vs corresponding rat hepatocytes treated with LPS-containing CM alone. NO: Nitric oxide; EGF: Epidermal growth factor; TGF: Transforming growth factor.
- Citation: Glanemann M, Knobeloch D, Ehnert S, Culmes M, Seeliger C, Seehofer D, Nussler AK. Hepatotropic growth factors protect hepatocytes during inflammation by upregulation of antioxidative systems. World J Gastroenterol 2011; 17(17): 2199-2205
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v17/i17/2199.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v17.i17.2199