Copyright
©2011 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. May 7, 2011; 17(17): 2199-2205
Published online May 7, 2011. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v17.i17.2199
Published online May 7, 2011. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v17.i17.2199
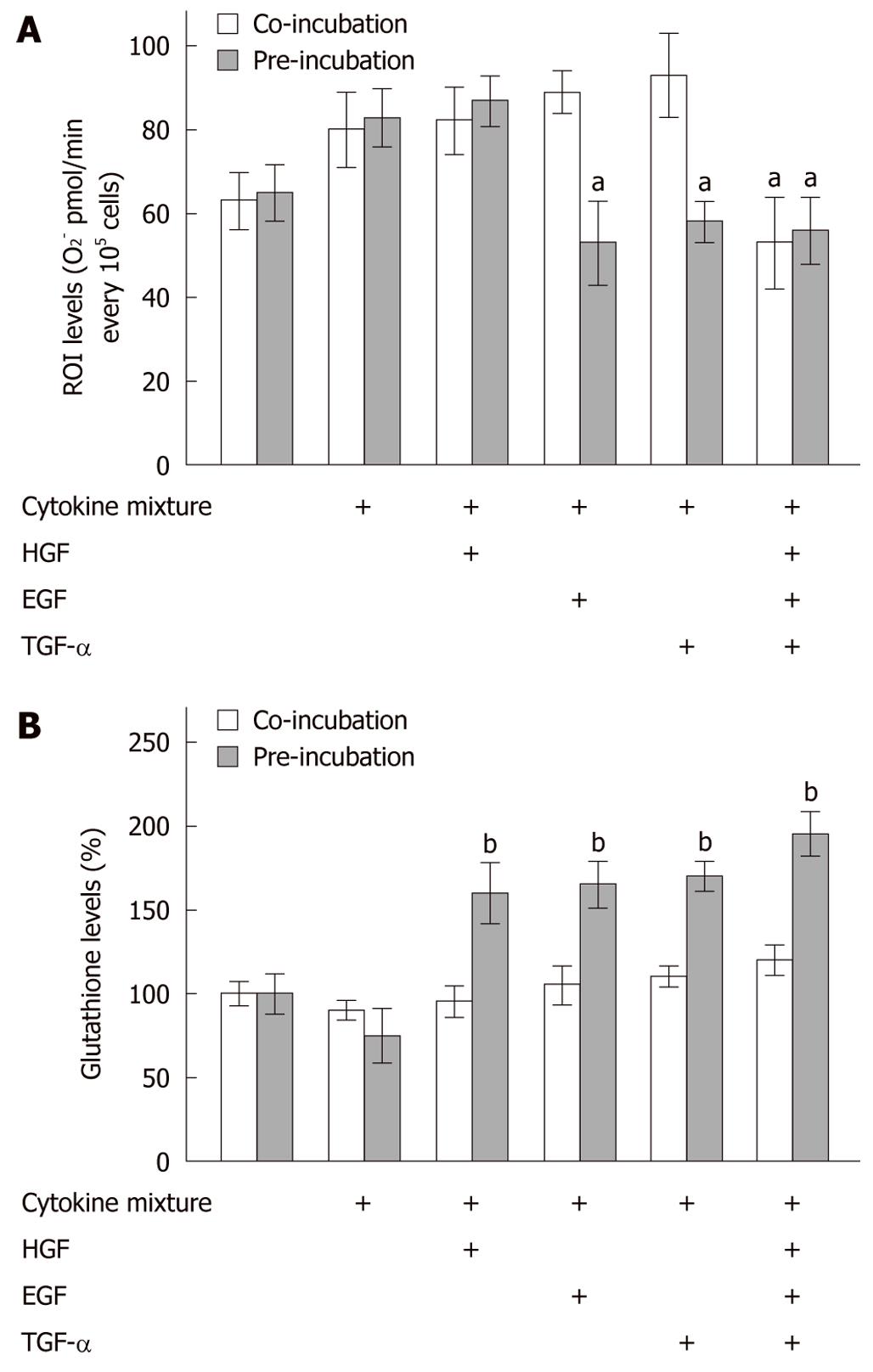
Figure 2 Increased oxidative stress in rat hepatocytes treated with lipopolysaccharide-containing cytokine mixture.
A: Treatment of primary rat hepatocytes (N = 5, n = 3) with lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-containing cytokine mixture (CM) for 24 h caused a slight increase in O2- production. B: Cellular glutathione levels were not significantly affected by this treatment. Co-incubation with single hepatocyte growth factor (HGF), epidermal growth factor (EGF) or transforming growth factor (TGF)-α did not reduce reactive oxygen intermediate (ROI) production significantly. Co-incubation with the hepatotropic growth factor mixture alone was able to reduce ROI production significantly. Furthermore, co-incubation with the growth factors did not alter cellular glutathione levels (empty bars). On the other hand, preincubation with these growth factors, individually or in combination, significantly reduced ROI production (except for pretreatment with HGF alone). Preincubation with the different growth factors increased cellular glutathione significantly (grey bars). aP < 0.05, bP < 0.001 vs corresponding rat hepatocytes treated with LPS-containing CM alone.
- Citation: Glanemann M, Knobeloch D, Ehnert S, Culmes M, Seeliger C, Seehofer D, Nussler AK. Hepatotropic growth factors protect hepatocytes during inflammation by upregulation of antioxidative systems. World J Gastroenterol 2011; 17(17): 2199-2205
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v17/i17/2199.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v17.i17.2199