Copyright
©2011 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. May 7, 2011; 17(17): 2161-2171
Published online May 7, 2011. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v17.i17.2161
Published online May 7, 2011. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v17.i17.2161
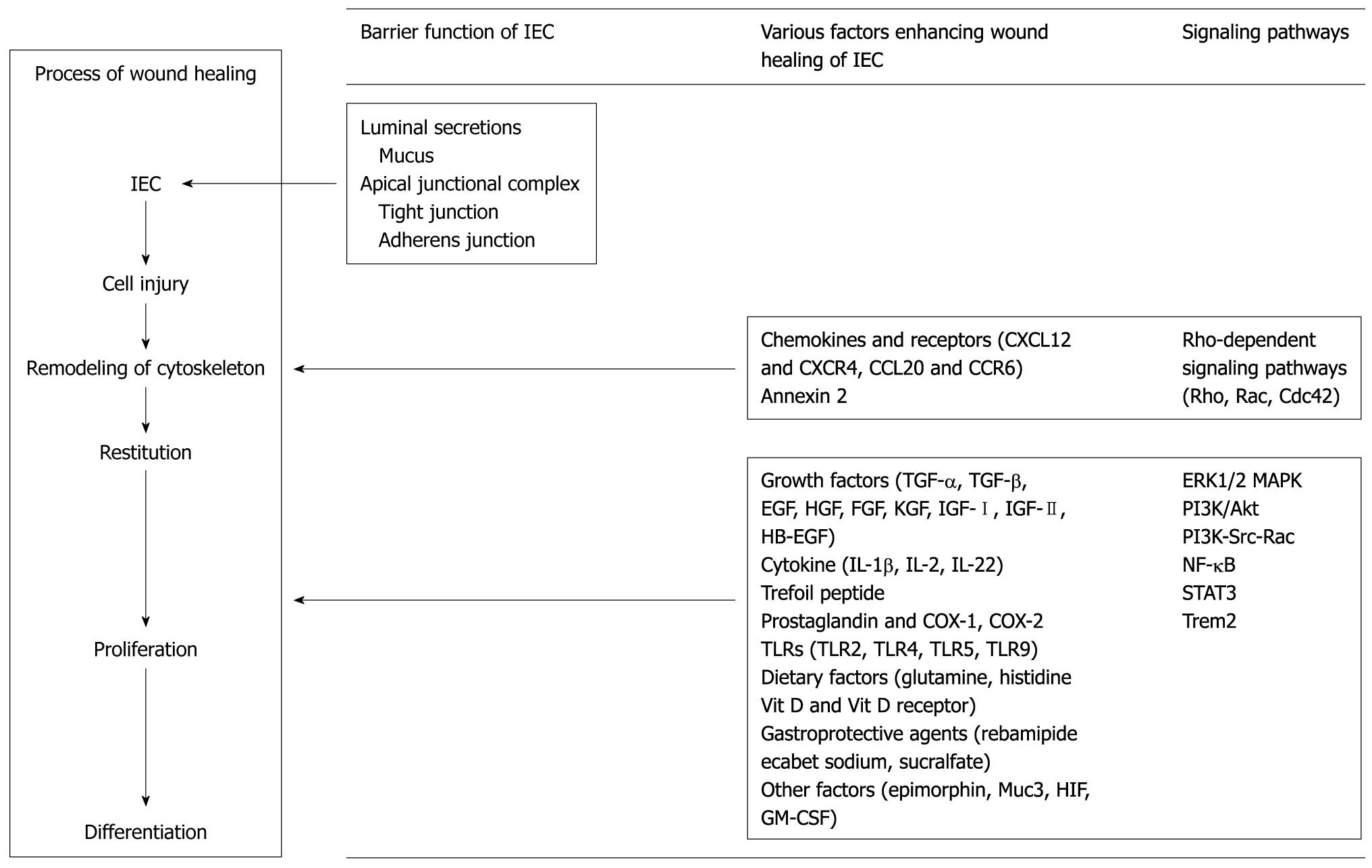
Figure 2 Various factors and signaling pathways contributing to the process of wound healing of intestinal epithelial cells and intestinal mucosa.
IEC: Intestinal epithelial cell; TGF: Transforming growth factor; EGF: Epidermal growth factor; HGF: Hepatocyte growth factor; FGF: Fibroblast growth factor; KGF: Keratinocyte growth factor; IGF: Insulin-like growth factor; HB-EGF: Heparin-binding epidermal growth factor; IL: Interleukin; COX: Cyclooxygenase; TLR: Toll-like receptor; HIF: Hypoxia-inducible factor; GM-CSF: Granulocyte-macrophage colony stimulating factor; ERK: Extracellular signal-regulated kinase; MAPK: Mitogen-activated protein kinase; PI3K: Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase; NF: Nuclear factor; STAT: Signal transducer and activator of transcription.
- Citation: Iizuka M, Konno S. Wound healing of intestinal epithelial cells. World J Gastroenterol 2011; 17(17): 2161-2171
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v17/i17/2161.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v17.i17.2161