Copyright
©2011 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Apr 21, 2011; 17(15): 2019-2027
Published online Apr 21, 2011. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v17.i15.2019
Published online Apr 21, 2011. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v17.i15.2019
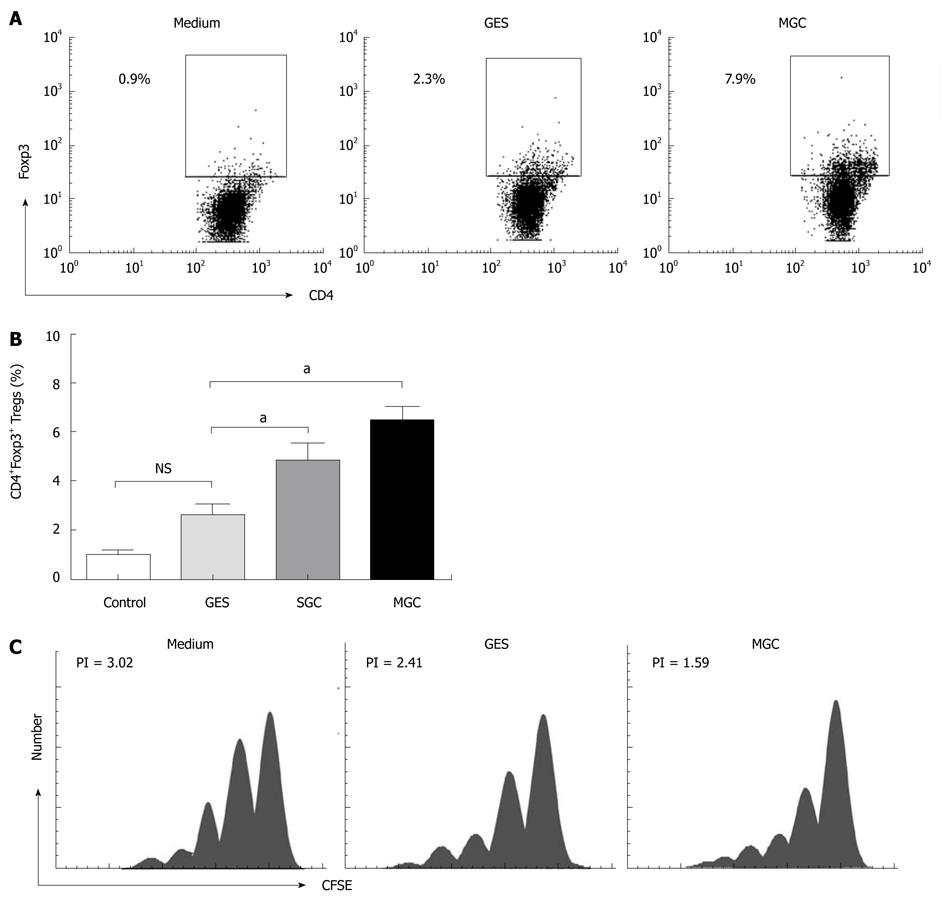
Figure 2 Gastric cancer cell supernatant mediates the conversion of CD4+CD25- T cell to CD4+Foxp3+ Tregs.
A: Representative flow cytometry analysis of CD4+Foxp3+ Tregs frequency in CD4+ T cells population following sorted CD4+CD25-CD127+ T cells co-culture with medium, GES, or MGC supernatants; B: Summarized data showed that both MGC and SGC supernatants induced higher CD4+Foxp3+ Tregs (aP < 0.05); C: After co-culture with MGC, GES or medium, CD4+CD25- T cells were placed in coculture with CFSE-labeled CD4+CD25-CD127+ T cells at a ratio of 1:1 in the presence of soluble anti-CD3/CD28 as well as IL-2. The representative data from three independent experiments are shown.
- Citation: Yuan XL, Chen L, Zhang TT, Ma YH, Zhou YL, Zhao Y, Wang WW, Dong P, Yu L, Zhang YY, Shen LS. Gastric cancer cells induce human CD4+Foxp3+ regulatory T cells through the production of TGF-β1. World J Gastroenterol 2011; 17(15): 2019-2027
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v17/i15/2019.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v17.i15.2019