Copyright
©2011 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Apr 14, 2011; 17(14): 1874-1878
Published online Apr 14, 2011. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v17.i14.1874
Published online Apr 14, 2011. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v17.i14.1874
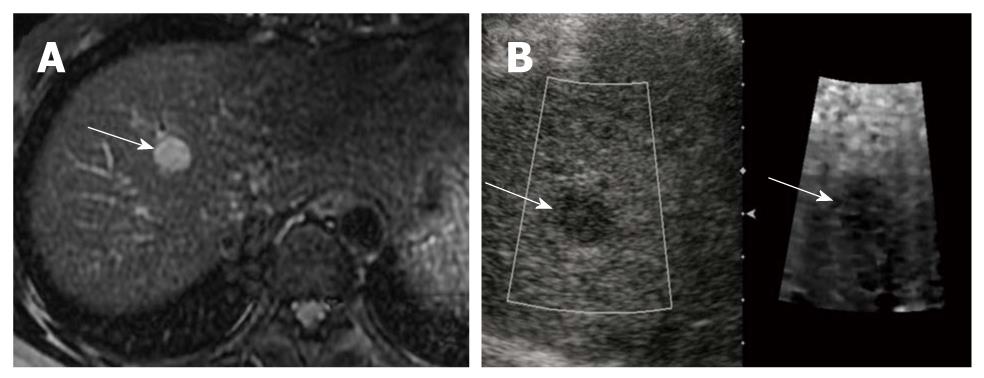
Figure 2 Hepatocellular carcinoma in a 45-year-old woman with underlying liver cirrhosis.
A: T2-weighted magnetic resonance image shows a high signal intensity hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) in segment 4 of the liver (arrow); B: On a B-mode image, the HCC is seen as an ovoid, hypoechoic mass (arrow), that appears darker (stiffer) than hepatic background on the acoustic radiation force impulse image (arrow). The shear wave velocity of HCC and surrounding hepatic parenchyma were measured as 2.20 m/s and 1.57 m/s, respectively (not shown).
- Citation: Kwon HJ, Kang MJ, Cho JH, Oh JY, Nam KJ, Han SY, Lee SW. Acoustic radiation force impulse elastography for hepatocellular carcinoma-associated radiofrequency ablation. World J Gastroenterol 2011; 17(14): 1874-1878
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v17/i14/1874.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v17.i14.1874