Copyright
©2011 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Apr 14, 2011; 17(14): 1874-1878
Published online Apr 14, 2011. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v17.i14.1874
Published online Apr 14, 2011. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v17.i14.1874
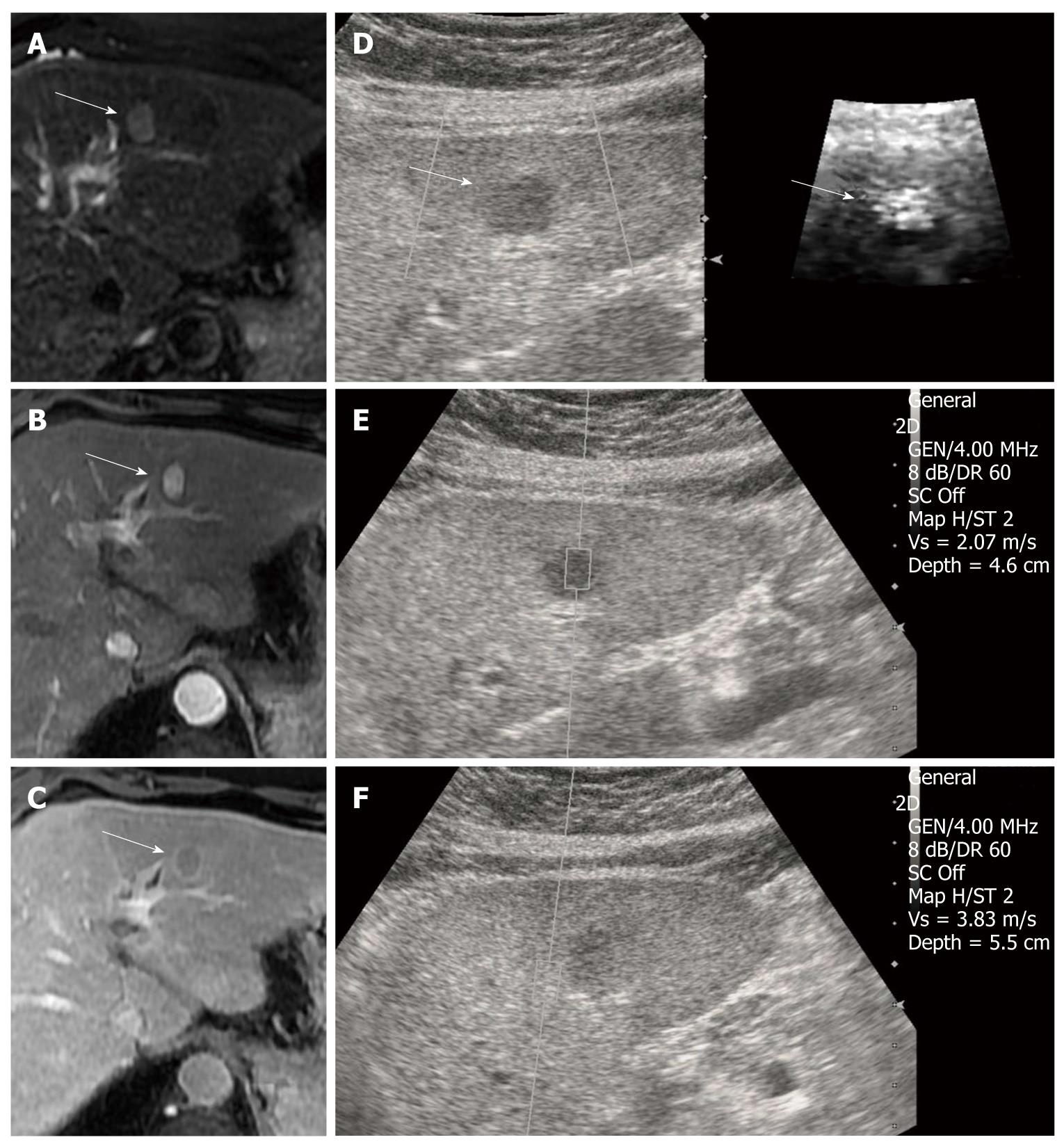
Figure 1 Hepatocellular carcinoma in a 59-year-old man with underlying liver cirrhosis.
A: T2-weighted magnetic resonance (MR) image shows a high signal intensity mass in segment 2 of the liver (arrow); B: On dynamic study, the mass revealed an arterial enhancement; C: Delayed wash-out, which is a typical finding of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) (arrow); D: On B-mode image, the HCC appears as a well defined, hypoechoic mass and the HCC have a bright (softer) color on the acoustic radiation force impulse (ARFI) image (arrows); E: The shear wave velocity (SWV) of HCC is 2.07 m/s; F: SWV of surrounding cirrhotic hepatic parenchyma measures 3.83 m/s. GEN: General; SC: Spatial compounding; Vs: Velocity.
- Citation: Kwon HJ, Kang MJ, Cho JH, Oh JY, Nam KJ, Han SY, Lee SW. Acoustic radiation force impulse elastography for hepatocellular carcinoma-associated radiofrequency ablation. World J Gastroenterol 2011; 17(14): 1874-1878
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v17/i14/1874.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v17.i14.1874