Copyright
©2011 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Apr 7, 2011; 17(13): 1739-1745
Published online Apr 7, 2011. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v17.i13.1739
Published online Apr 7, 2011. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v17.i13.1739
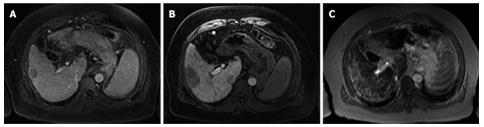
Figure 1 A 49-year-old man with hepatic cirrhosis due to chronic hepatitis B and C infection.
Histology obtained following liver transplantation confirmed the diagnosis of a multifocal hepatocellular carcinoma. A: Magnetic resonance imaging (T1-weighted VIBE) during early venous phase shows a low signal intensity nodule with a diameter of approximately 3 cm in segment VIII/V; B: SPIO-enhanced T2-weighted fast image shows an area of increased signal intensity (segment VIII/V) within the otherwise lower but very inhomogenous signal of the liver parenchyma with profound cirrhosis; C: MR-AP (T1-weighted VIBE) during early venous phase displays an area of decreased enhancement (approx. 4.5 cm diameter) in segment VIII/V. Note the multiple smaller hypointense lesions in segments VII/VI. SPIO: Superparamagnetic iron oxide-enhanced.
- Citation: Rennert J, Jung EM, Schreyer AG, Hoffstetter P, Heiss P, Feuerbach S, Zorger N. MR-arterioportography: A new technical approach for detection of liver lesions. World J Gastroenterol 2011; 17(13): 1739-1745
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v17/i13/1739.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v17.i13.1739