Copyright
©2011 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Mar 28, 2011; 17(12): 1584-1593
Published online Mar 28, 2011. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v17.i12.1584
Published online Mar 28, 2011. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v17.i12.1584
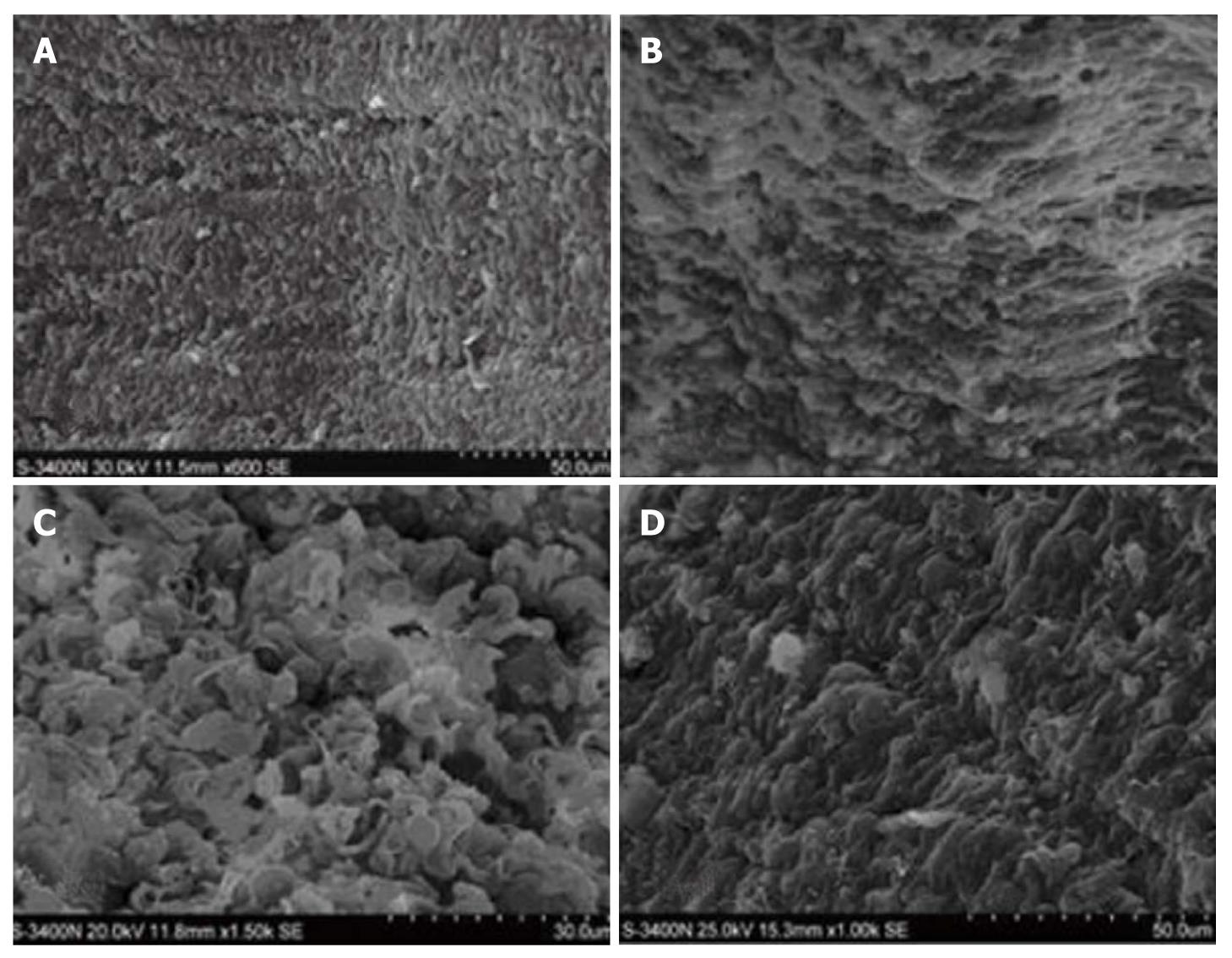
Figure 3 Scanning electron microscopy.
A smooth surface of intestinal mucosa with a clear structure as well as complete and orderly villi in group C (A) (× 6900), atrophic epithelial structure of intestinal mucosa and lodging villi accompanying a rough surface with disordered villi and widened villous spaces in group H (B) (× 6900), severely injured intestinal mucosa as well as disc-shaped cells and cellulose in mucosal defects along with evident atrophy and disordered villi with widened villous spaces and exfoliated microvilli in group HH (C) (× 11 500), almost intact intestinal mucosa with orderly villi and less effusion but no disc-shaped cells and cellulose in group HG (D) (× 11 500).
- Citation: Zhou QQ, Yang DZ, Luo YJ, Li SZ, Liu FY, Wang GS. Over-starvation aggravates intestinal injury and promotes bacterial and endotoxin translocation under high-altitude hypoxic environment. World J Gastroenterol 2011; 17(12): 1584-1593
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v17/i12/1584.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v17.i12.1584