Copyright
©2011 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Mar 14, 2011; 17(10): 1326-1331
Published online Mar 14, 2011. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v17.i10.1326
Published online Mar 14, 2011. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v17.i10.1326
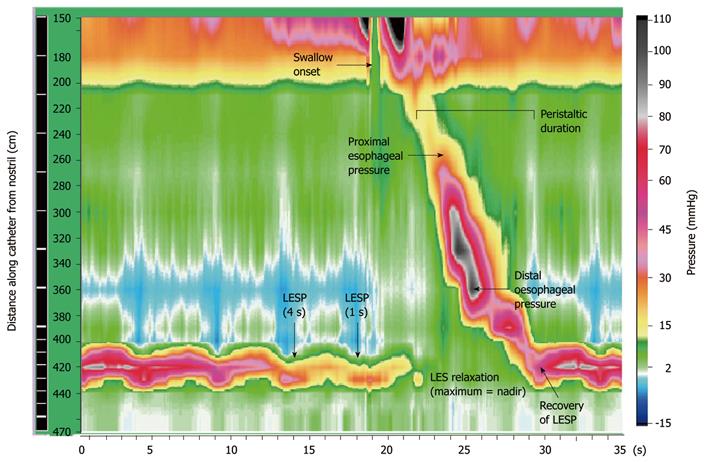
Figure 1 Example of swallow pressure topography spanning from the pharynx (15-20 cm) to stomach (44-47 cm), in a young patient with normal peristalsis and lower esophageal sphincter relaxation.
Pressure data (amplitudes shown by colour gradient) are displayed with time on the x-axis and location of sensors on the y-axis. Points of measurement for motility parameters are indicated with arrows. Pressure sensors located in the region of the lower esophageal sphincter (LES) are spaced 1 cm apart, spanning a 6 cm segment. LESP: Lower esophageal sphincter pressure.
- Citation: Besanko LK, Burgstad CM, Mountifield R, Andrews JM, Heddle R, Checklin H, Fraser RJ. Lower esophageal sphincter relaxation is impaired in older patients with dysphagia. World J Gastroenterol 2011; 17(10): 1326-1331
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v17/i10/1326.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v17.i10.1326