Copyright
©2010 Baishideng.
World J Gastroenterol. Mar 7, 2010; 16(9): 1097-1103
Published online Mar 7, 2010. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v16.i9.1097
Published online Mar 7, 2010. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v16.i9.1097
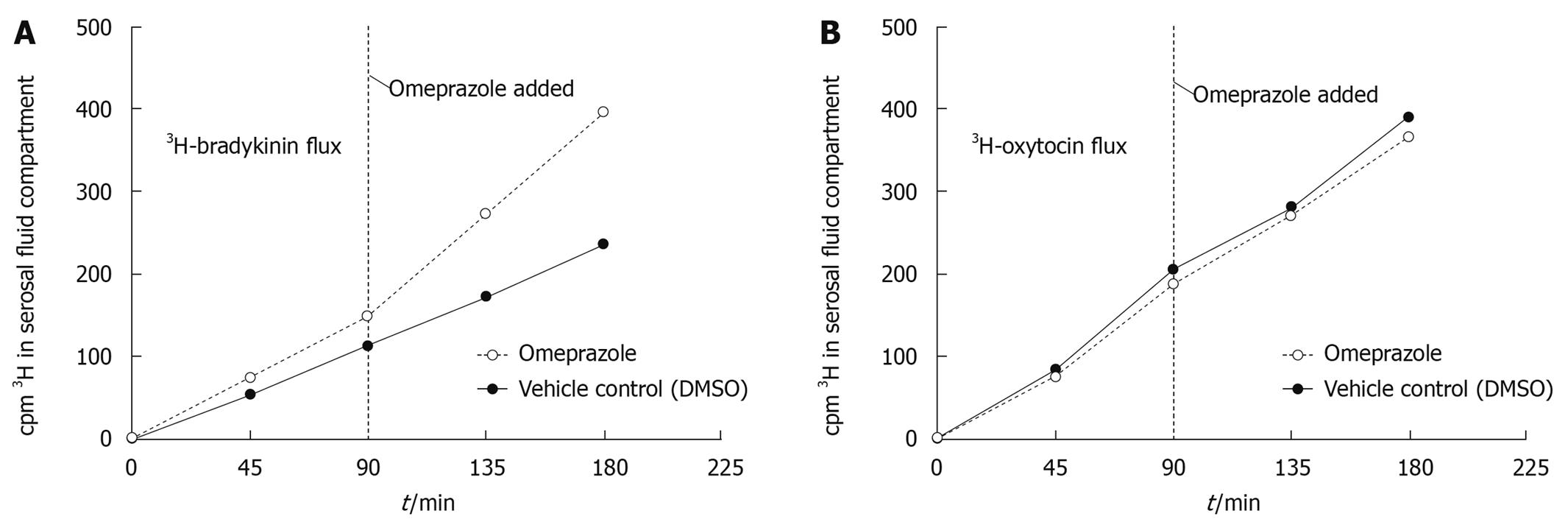
Figure 3 3H-bradykinin (panel A) or 3H-oxytocin (panel B) was added to the mucosal fluid compartment at t = 0 to begin the flux period of 180 min.
Omeprazole or DMSO was added to the tissue 90 min after the addition of 3H-peptide. Samples were taken every 45 min for the total 180 min flux period (pre- and post-omeprazole/DMSO) from the serosal fluid compartment for LSC and TLC. Omeprazole increases the rate at which total radioactivity crosses the gastric mucosa compared to the paired vehicle control (DMSO) in a 3H-bradykinin flux experiment (panel A) whereas total radioactivity crossing the tissue in a 3H-oxytocin flux experiment (panel B) remains unchanged after the addition of omeprazole or DMSO. Both panel A and panel B represent two separate experiments and animals.
- Citation: Gabello M, Valenzano MC, Zurbach EP, Mullin JM. Omeprazole induces gastric transmucosal permeability to the peptide bradykinin. World J Gastroenterol 2010; 16(9): 1097-1103
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v16/i9/1097.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v16.i9.1097