Copyright
©2010 Baishideng.
World J Gastroenterol. Feb 21, 2010; 16(7): 846-853
Published online Feb 21, 2010. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v16.i7.846
Published online Feb 21, 2010. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v16.i7.846
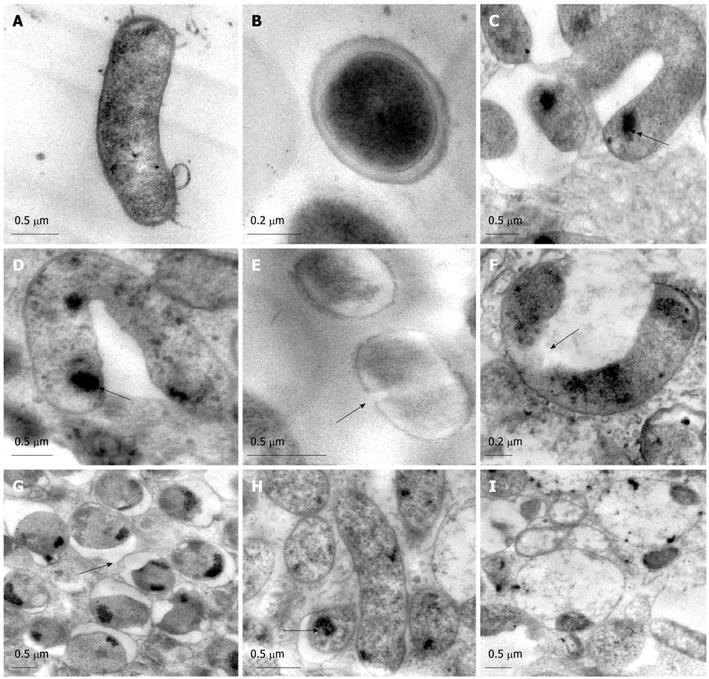
Figure 2 Transmission electron microscopy (TEM).
TEM showing rod-shaped H. pylori (A), well-distributed cytoplasm and moderate electron density (B), U-shaped (C, arrow) and V-shaped (D, arrow) H. pylori, non-integrity (E, arrow) and abscission (F, arrow) of H. pylori cell wall, outer membrane separated from the cytoplasmic membrane (G, arrow), decreased electron density in cytoplasm (H, arrow), and cell lysis (I) after treatment with celecoxib.
-
Citation: Wang J, Wang WH, Li J, Liu FX. Celecoxib inhibits
Helicobacter pylori colonization-related factors. World J Gastroenterol 2010; 16(7): 846-853 - URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v16/i7/846.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v16.i7.846