Copyright
©2010 Baishideng.
World J Gastroenterol. Feb 14, 2010; 16(6): 713-722
Published online Feb 14, 2010. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v16.i6.713
Published online Feb 14, 2010. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v16.i6.713
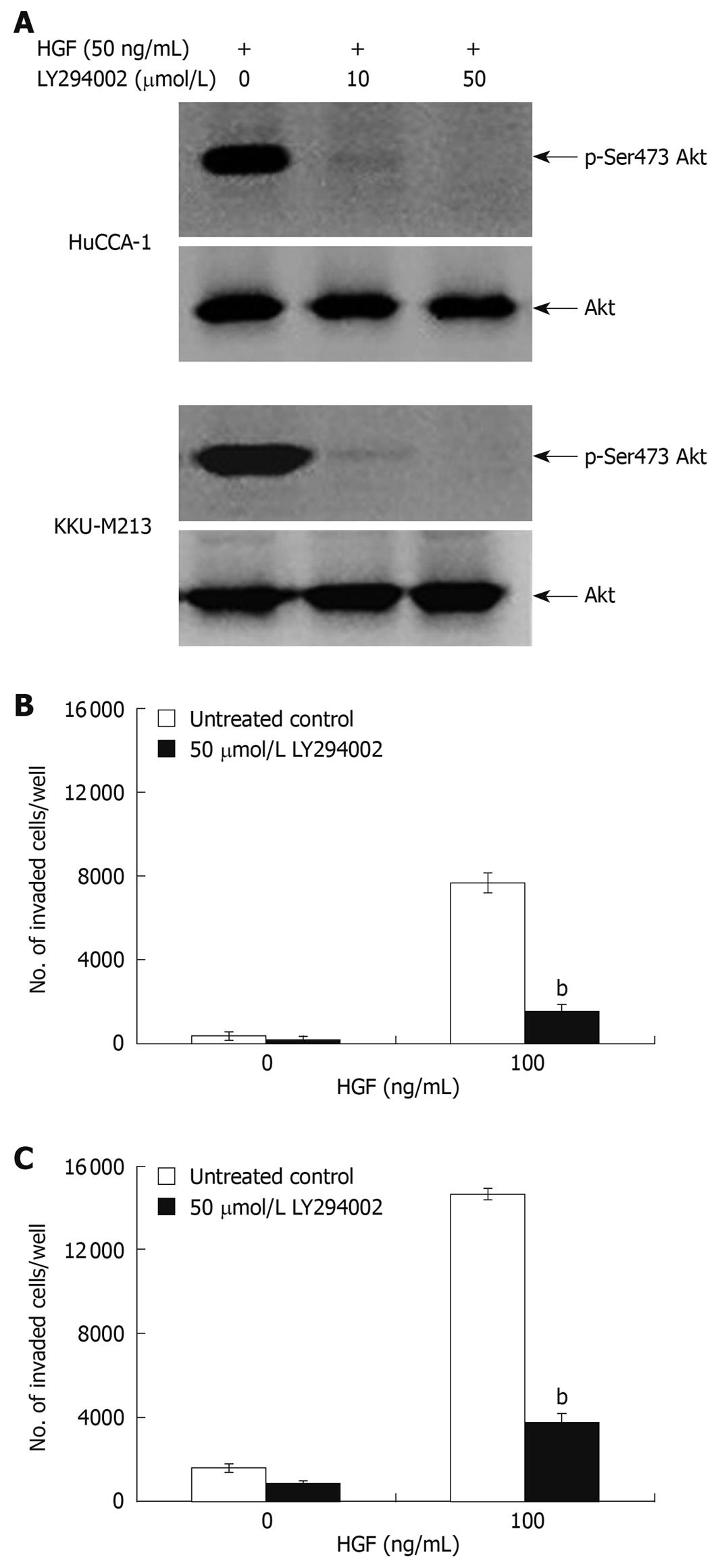
Figure 6 Suppression of HGF-induced cholangiocarcinoma cell invasiveness by PI3-kinase inhibitor, LY294002.
HuCCA-1 and KKU-M213 cells were treated with 50 ng/mL HGF in the absence (control) or presence of 10 and 50 μmol/L LY294002 for 6 h, and subsequently Akt phosphorylation was determined by Western blotting (A). In vitro invasion of HuCCA-1 (B) and KKU-M213 (C) cells was evaluated in the absence or presence of HGF with or without 50 μmol/L LY294002. Numbers of invaded cells are presented as mean ± SE of results obtained from three independent experiments. bP < 0.01 vs control.
- Citation: Menakongka A, Suthiphongchai T. Involvement of PI3K and ERK1/2 pathways in hepatocyte growth factor-induced cholangiocarcinoma cell invasion. World J Gastroenterol 2010; 16(6): 713-722
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v16/i6/713.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v16.i6.713