Copyright
©2010 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Dec 28, 2010; 16(48): 6079-6086
Published online Dec 28, 2010. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v16.i48.6079
Published online Dec 28, 2010. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v16.i48.6079
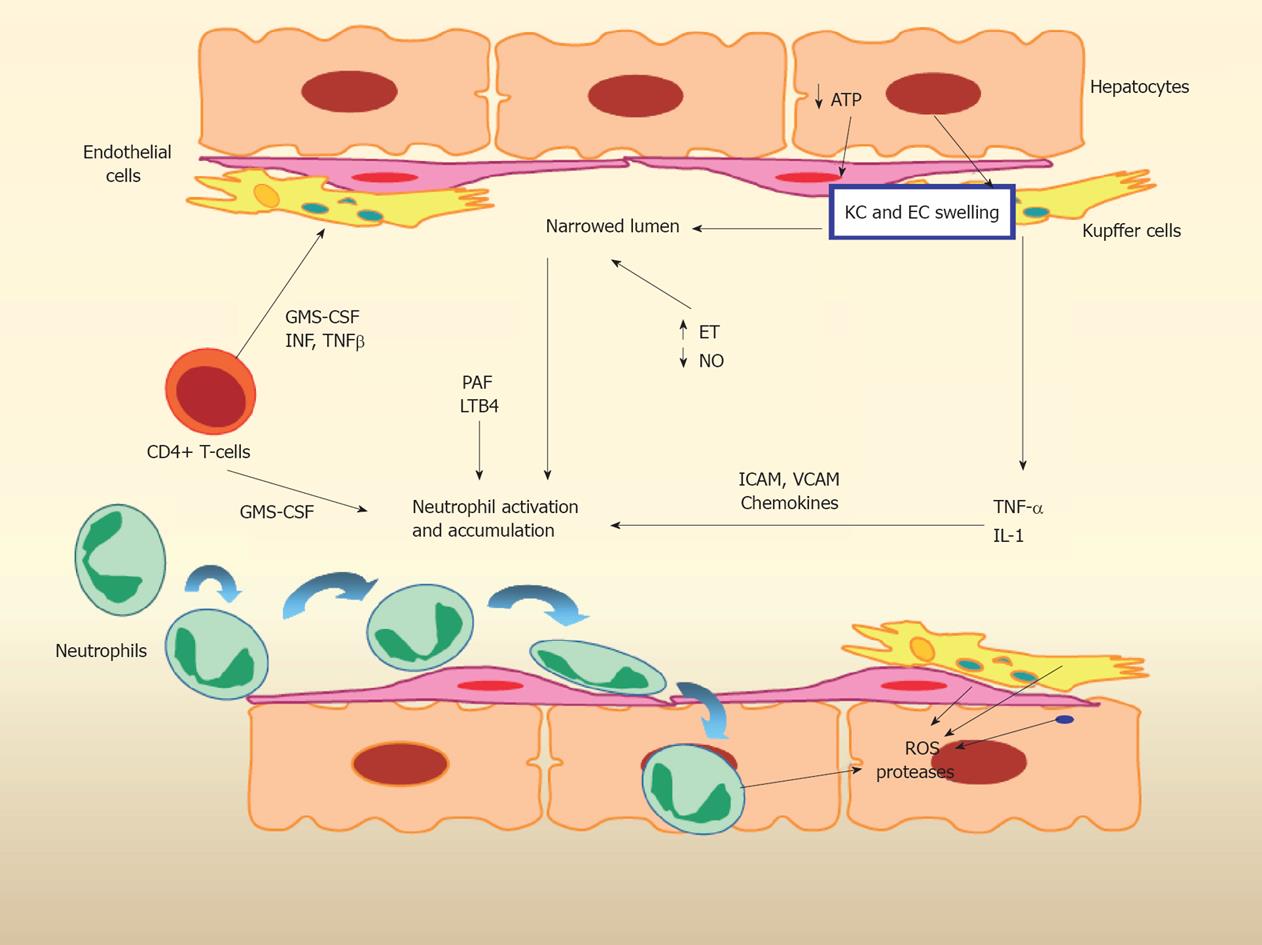
Figure 1 Multifaceted hepatic ischemia-reperfusion injury.
Kupffer and endothelial cells produce cytokines and chemokines, recruiting neutrophils that further accentuate injury. EC: Endothelial cell; KC: Kupffer cell; ATP: Adenosine triphosphate; TNF: Tumor necrosis factor; IL: Interleukin; ICAM: Intercellular adhesion molecule; VCAM: Vascular adhesion molecule; PAF: Platelet activation factor; LTB4: Leukotriene B4; GMS-CSF: Granulocyte macrophage colony stimulating factor; INF: Interferon; ROS: Reactive oxygen species (Courtesy of Dr. Joan Rosello-Catafau, Barcelona, Spain).
- Citation: Siriussawakul A, Zaky A, Lang JD. Role of nitric oxide in hepatic ischemia-reperfusion injury. World J Gastroenterol 2010; 16(48): 6079-6086
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v16/i48/6079.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v16.i48.6079