Copyright
©2010 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Dec 14, 2010; 16(46): 5852-5860
Published online Dec 14, 2010. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v16.i46.5852
Published online Dec 14, 2010. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v16.i46.5852
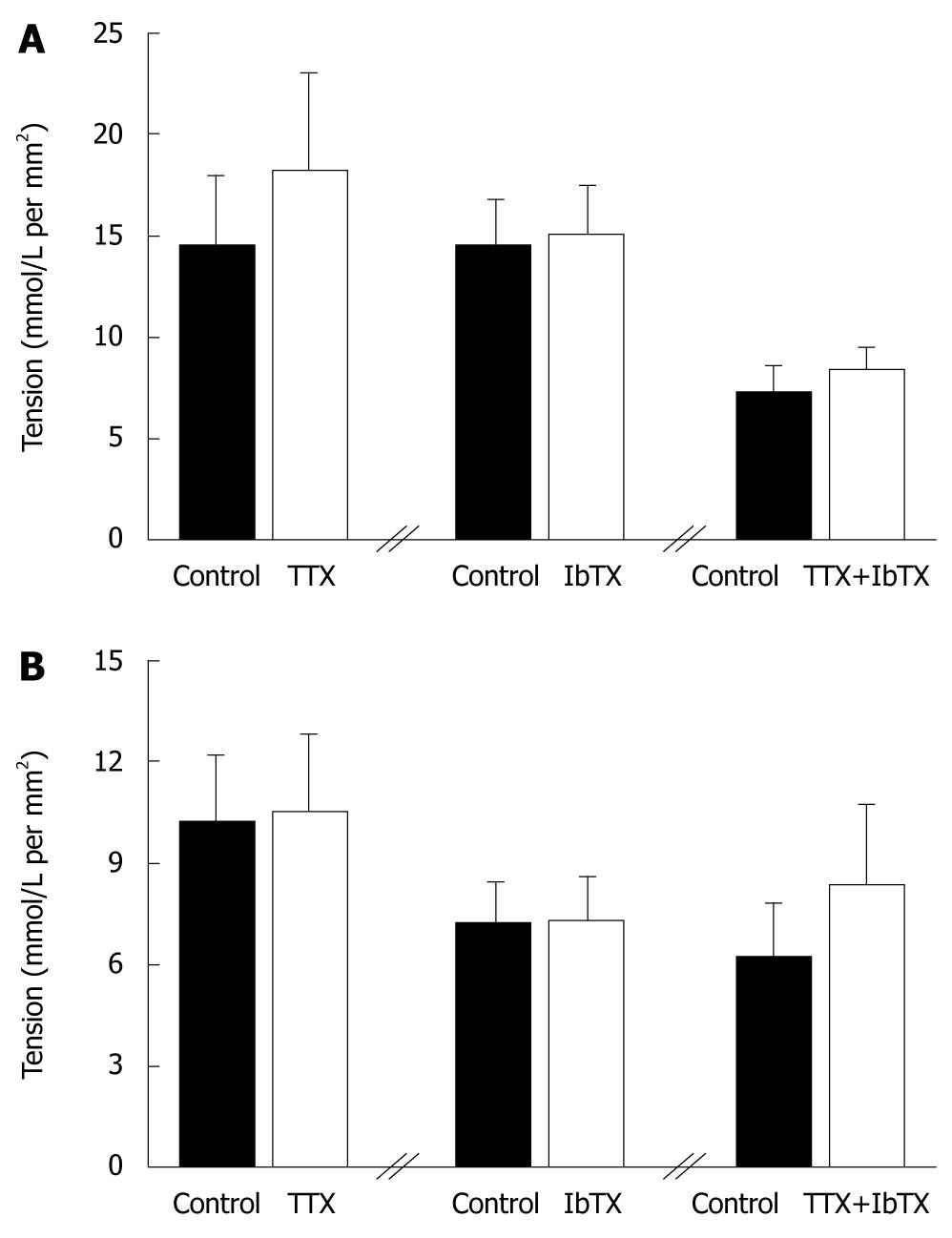
Figure 4 Effect of the blockade of the BKCa channel with iberiotoxin (10-7 mol/L) of lower esophageal sphincter (A) circular (n = 6-8) and (B) sling (n = 7-11) smooth muscle tone with intact nerves or blocked with tetrodotoxin (10-6 mol/L).
A: For the circular muscle, tetrodotoxin (TTX) or iberiotoxin (IbTX) did not significantly change the resting tension (P > 0.05). The combined blockade of the nerves and the BKCa channel also resulted in no significant change of the overall muscle tone (P > 0.05); B: Similarly, for the sling muscle, TTX, IbTX or TTX and IbTX together did not significantly modulate the basal resting tone (P > 0.05). //: Separates different experiments.
- Citation: L’Heureux MC, Muinuddin A, Gaisano HY, Diamant NE. Nitric oxide activation of a potassium channel (BKCa) in feline lower esophageal sphincter. World J Gastroenterol 2010; 16(46): 5852-5860
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v16/i46/5852.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v16.i46.5852