Copyright
©2010 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Dec 14, 2010; 16(46): 5779-5789
Published online Dec 14, 2010. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v16.i46.5779
Published online Dec 14, 2010. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v16.i46.5779
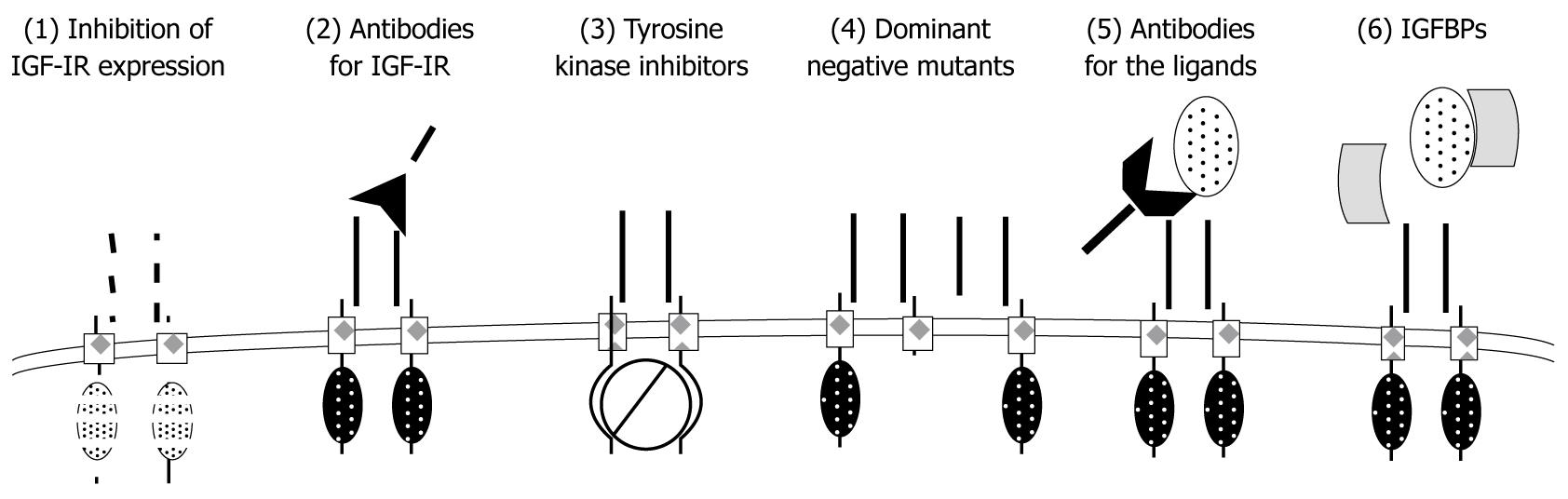
Figure 4 The summary of strategies to inactivate type I insulin-like growth factor receptor system.
(1) Inhibition of type I insulin-like growth factor receptor (IGF-IR) protein expression by blocking its translation [with antisense oligodeoxynucleotides and short interfering RNA (siRNA)]; (2) IGF-IR function can be blocked with inactivating monoclonal antibodies (mAb); (3) The tyrosine kinase activity of IGF-IR can be abolished with small-molecule inhibitors (TKI); (4) IGF-IR mutants lacking β-subunits can act as dominant-negative (dn) receptors; (5) Ligand availability can be reduced by mAb for IGFs; and (6) IGF binding proteins (IGFBPs) can reduce active forms of IGFs.
- Citation: Adachi Y, Yamamoto H, Ohashi H, Endo T, Carbone DP, Imai K, Shinomura Y. A candidate targeting molecule of insulin-like growth factor-I receptor for gastrointestinal cancers. World J Gastroenterol 2010; 16(46): 5779-5789
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v16/i46/5779.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v16.i46.5779