Copyright
©2010 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Dec 7, 2010; 16(45): 5759-5765
Published online Dec 7, 2010. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v16.i45.5759
Published online Dec 7, 2010. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v16.i45.5759
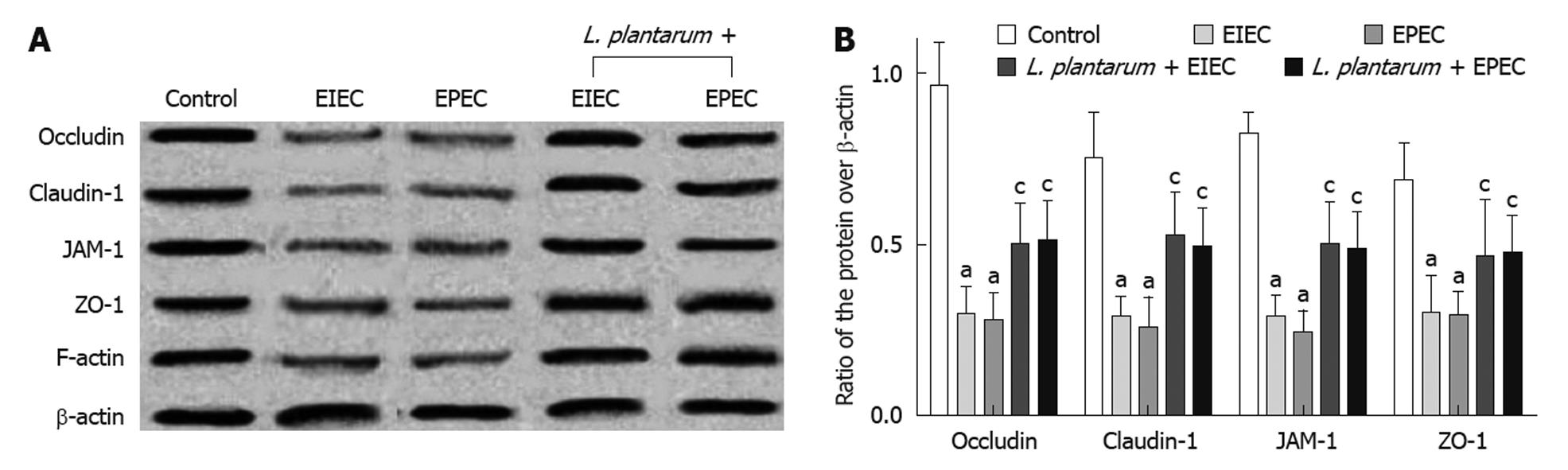
Figure 3 Lactobacillus plantarum prevented the decrease in the expression of tight junction proteins in NCM460 cells induced by enteroinvasive Escherichia coli or enteropathogenic Escherichia coli detected by Western blotting.
A: The expression level of tight junction (TJ) proteins was high, including claudin-1, occludin, JAM-1 and ZO-1, in the control group. However, in the enteroinvasive Escherichia coli (EIEC) or enteropathogenic Escherichia coli (EPEC) group, TJ proteins were significantly decreased compared with the control group, which was not observed in the Lactobacillus plantarum (L. plantarum) group; B: Semi-quantitative analysis of Western blotting showed similar results. The data at each time point represent the mean ± SD obtained from four individual NCM460 monolayers. aP < 0.05 vs control group; cP < 0.05 vs corresponding EIEC or EPEC group.
-
Citation: Liu ZH, Shen TY, Zhang P, Ma YL, Moyer MP, Qin HL. Protective effects of
Lactobacillus plantarum against epithelial barrier dysfunction of human colon cell line NCM460. World J Gastroenterol 2010; 16(45): 5759-5765 - URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v16/i45/5759.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v16.i45.5759