Copyright
©2010 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Nov 28, 2010; 16(44): 5582-5587
Published online Nov 28, 2010. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v16.i44.5582
Published online Nov 28, 2010. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v16.i44.5582
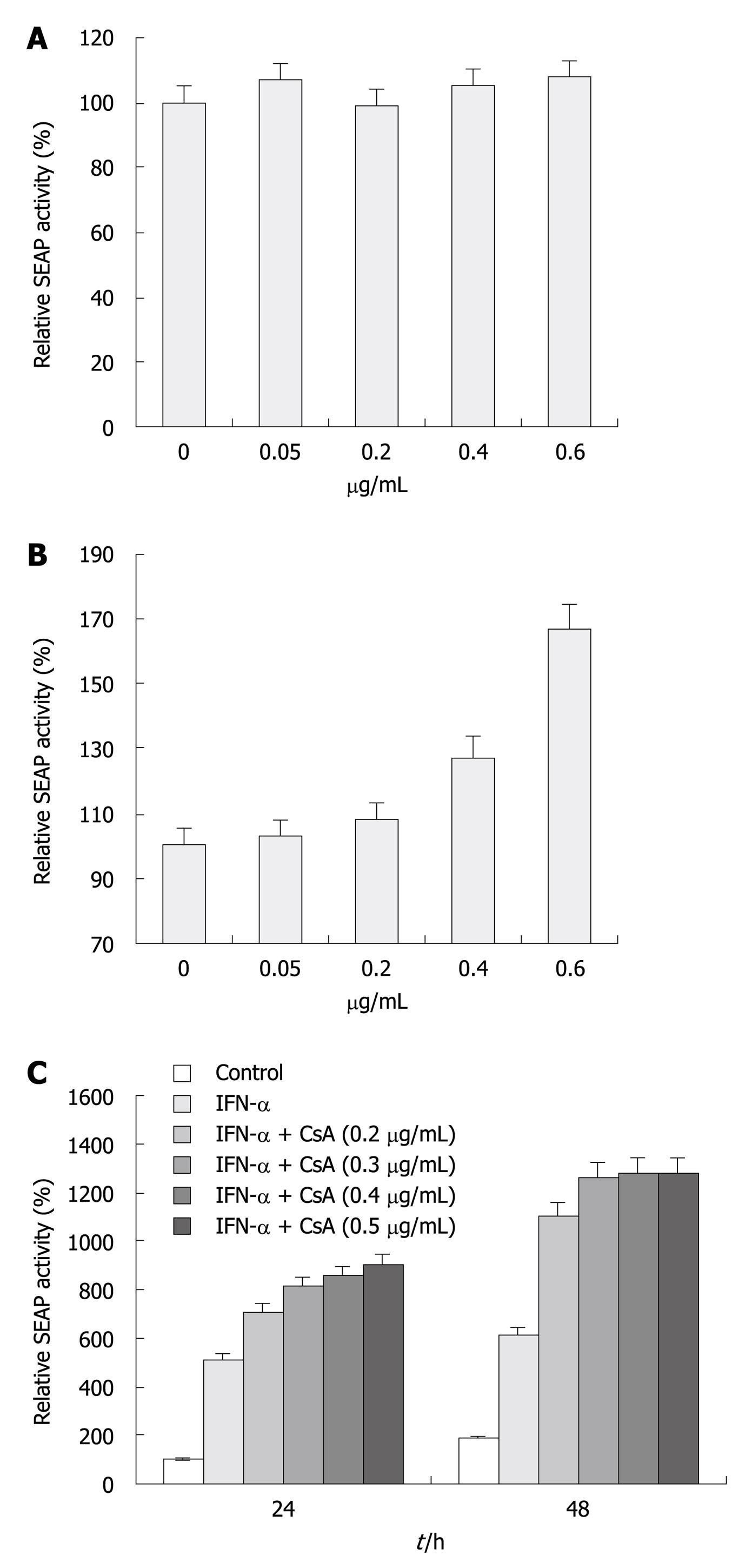
Figure 4 Inhibitory effect of cyclosporine A on hepatitis C virus replication and its combination effect with interferon-α.
A, B: Increase of secreted placental alkaline phosphatase (SEAP) activity in enhanced yellow fluorescent protein (eYFP)-mitochondrial antiviral signaling protein (MAVS) and interferon (IFN)-β-SEAP co-transfected Huh7.5 (P > 0.05) and replicon (P < 0.05) cells treated with cyclosporine A (CsA). Before transfection, Huh7.5 and replicon cells were incubated with CsA at 0, 0.05, 0.2, 0.4 and 0.6 μg/mL for 48 h. SEAP activity was measured at 24 h post-transfection in the presence of CsA. The percentage increase in SEAP activity relative to the untreated controls was plotted. Bars indicate SD (n = 3); C: IFN-α in combination with CsA therapy enhanced its inhibitory effect. Replicon cells were incubated with IFN-α (100 IU/mL) in combination with CsA at 0, 0.2, 0.3, 0.4 and 0.5 μg/mL for 48 h, and co-transfected with eYFP-MAVS and IFN-β-SEAP; pRL-TK was co-transfected to normalize transfection efficiency. SEAP activity was measured at 24 and 48 h post-transfection in the presence of IFN-α and CsA. The percentage increase of SEAP activity relative to the untreated controls was plotted. Bars indicate SD (n = 3).
- Citation: Fu QX, Wang LC, Jia SZ, Gao B, Zhou Y, Du J, Wang YL, Wang XH, Peng JC, Zhan LS. Screening compounds against HCV based on MAVS/IFN-β pathway in a replicon model. World J Gastroenterol 2010; 16(44): 5582-5587
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v16/i44/5582.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v16.i44.5582