Copyright
©2010 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Nov 28, 2010; 16(44): 5565-5581
Published online Nov 28, 2010. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v16.i44.5565
Published online Nov 28, 2010. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v16.i44.5565
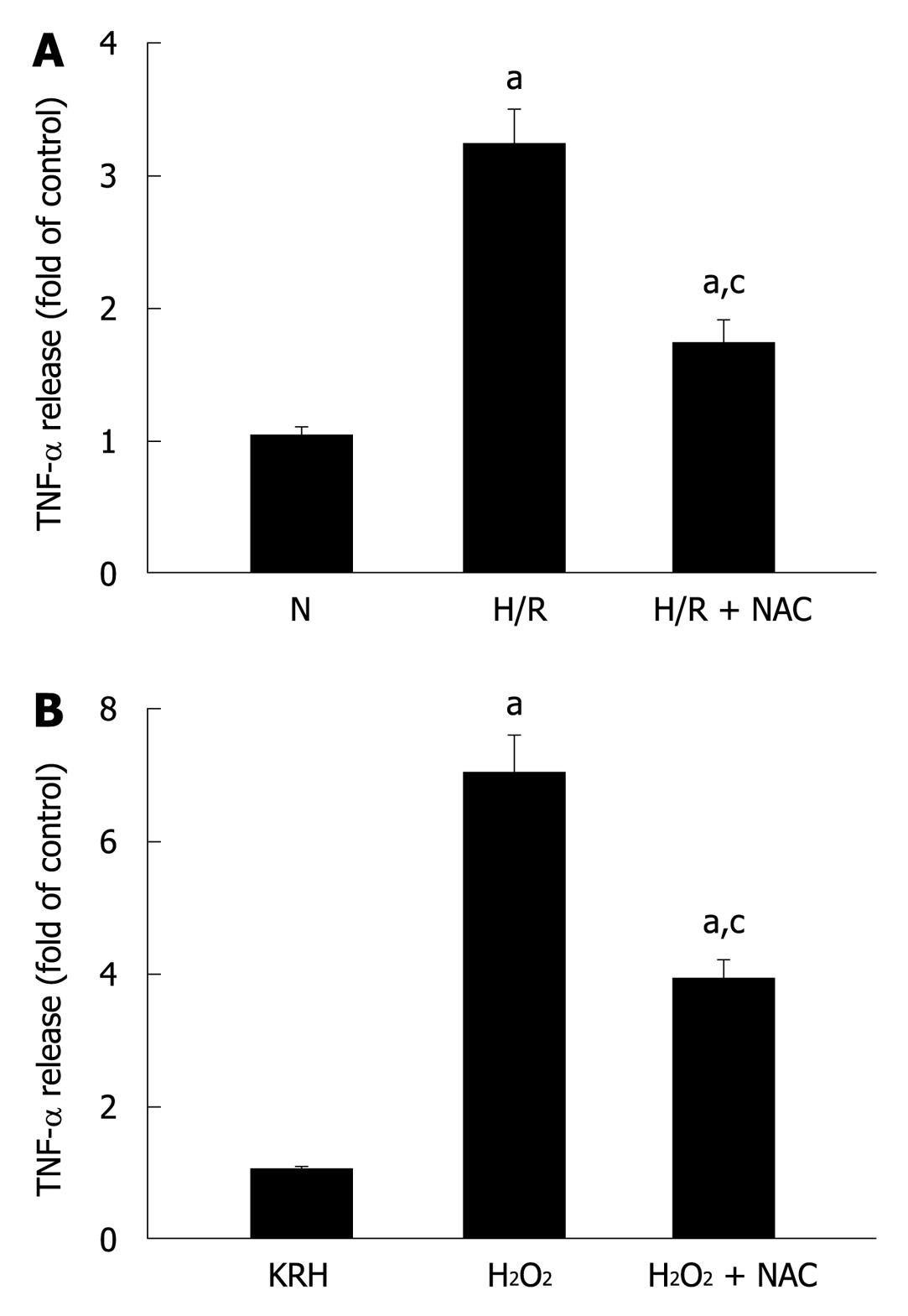
Figure 4 Pancreatic acinar cells secrete tumor necrosis factor-α in response to different stressful stimuli.
A: Isolated pancreatic acini were cultured in normoxic (N) conditions for 3.5 h or under hypoxia followed by normoxia-reoxygenation (H/R) for 30 min and 3 h, respectively, in the absence or presence of N-acetyl-cysteine (NAC) (30 mmol/L); B: Isolated pancreatic acini were cultured in Krebs-Ringer-HEPES (KRH) (vehicle-control) or stimulated with H2O2 (50 μmol/L) for 3 h in the absence or presence of NAC (30 mmol/L); A and B: TNF-α released into the supernatant was determined by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay using the respective assay kit. Results are expressed as fold of control and correspond to the mean ± SE from four independent experiments, with samples performed in triplicate. aP < 0.05 vs normoxia (A) or to KRH (B); cP < 0.05 vs H/R (A) or H2O2 (B).
- Citation: Binker MG, Binker-Cosen AA, Richards D, Gaisano HY, de Cosen RH, Cosen-Binker LI. Chronic stress sensitizes rats to pancreatitis induced by cerulein: Role of TNF-α. World J Gastroenterol 2010; 16(44): 5565-5581
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v16/i44/5565.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v16.i44.5565