Copyright
©2010 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Nov 14, 2010; 16(42): 5306-5316
Published online Nov 14, 2010. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v16.i42.5306
Published online Nov 14, 2010. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v16.i42.5306
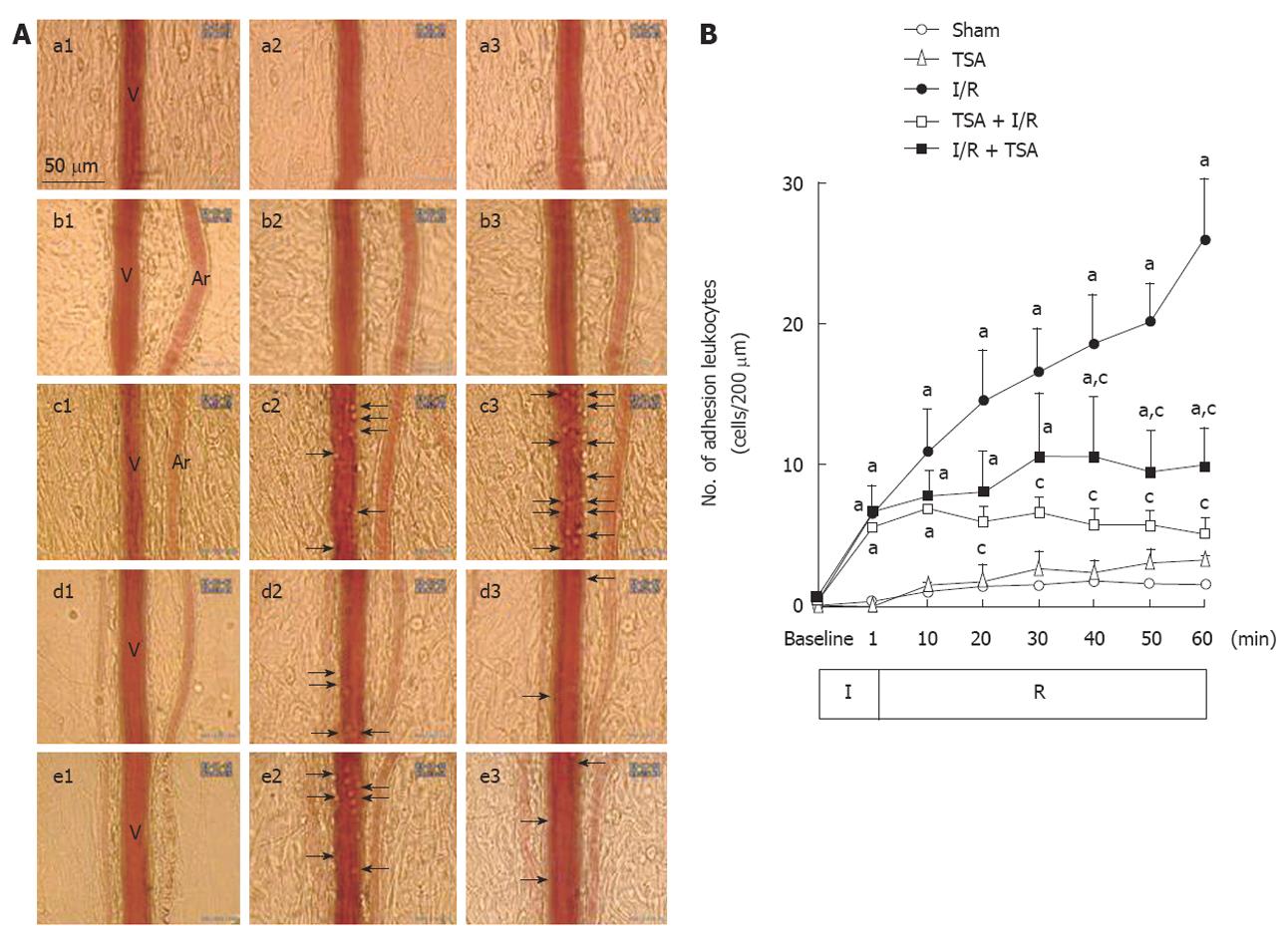
Figure 2 The effect of pre-treatment and post-treatment of total salvianolic acid on ischemia-reperfusion-induced leukocyte adhesion to the rat mesenteric venular wall.
A: Representative images illustrating the effect of pre-treatment and post-treatment of total salvianolic acid (TSA) on leukocyte adhesion to the venular wall induced by ischemia-reperfusion (I/R) in rat mesentery. a1-a3: Rat mesentery images of Sham group at baseline, 10 and 60 min, respectively. b1-b3: Rat mesentery images of TSA group at baseline, 10 and 60 min, respectively. c1-c3: Rat mesentery images of I/R group at baseline, 10 and 60 min, respectively. d1-d3: Rat mesentery images of rat mesentery of TSA + I/R group at baseline, 10 and 60 min respectively. e1-e3: Rat mesentery images of I/R + TSA group at baseline, 10 and 60 min, respectively. V: Rat mesenteric venule; Ar: Rat mesenteric arteriole; Arrows: Leukocytes adhered to the venular wall; B: Time course of changes in the number of leukocytes adherent to the mesenteric venules of rat. The number of adherent leukocytes was expressed as the number of cells per 200 μm of venules. Sham: Sham group; TSA: TSA group; I/R: I/R group; TSA + I/R: TSA plus I/R group; I/R + TSA: I/R plus TSA group. Data was expressed as mean ± SE of six animals. aP < 0.05 vs sham group; cP < 0.05 vs I/R alone.
- Citation: Wang MX, Liu YY, Hu BH, Wei XH, Chang X, Sun K, Fan JY, Liao FL, Wang CS, Zheng J, Han JY. Total salvianolic acid improves ischemia-reperfusion-induced microcirculatory disturbance in rat mesentery. World J Gastroenterol 2010; 16(42): 5306-5316
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v16/i42/5306.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v16.i42.5306