Copyright
©2010 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Oct 28, 2010; 16(40): 5092-5103
Published online Oct 28, 2010. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v16.i40.5092
Published online Oct 28, 2010. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v16.i40.5092
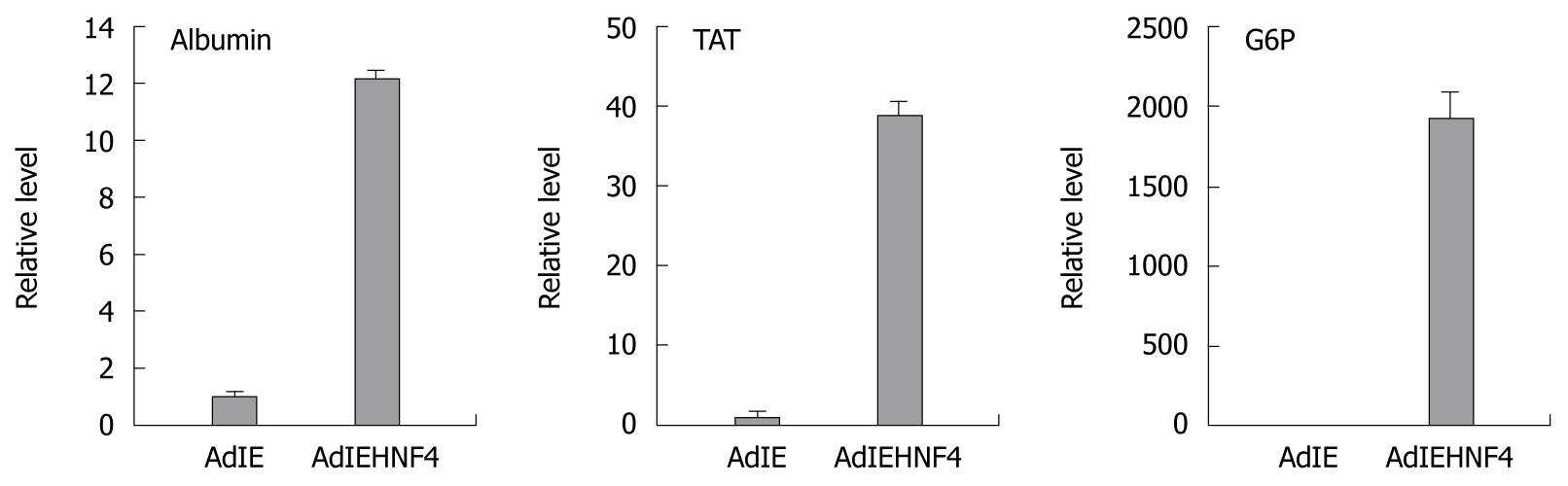
Figure 5 Detection of liver-specific genes in hepatocyte nuclear factor-4α overexpressing induced mesenchymal stem cells by real-time reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction.
The induced mesenchymal stem cells (8 wk post-induction) were infected with adenovirus containing rHNF-4α gene (indicated as AdIEHNF4) or parental control adenovirus (indicated as AdIE). The relative level of each gene in the control group was set to 1. The induction effect of HNF-4α on the expression of liver-specific genes was represented as Albumin, tyrosine-aminotransferase (TAT), and glucose 6-phosphatase (G6P), respectively. The amount of input RNA was normalized using the hypoxanthine-guanine phosphoribosyltransferase gene. Each column represents the mean ± SD of three independent experiments and the induction fold for each gene was significant (P < 0.05). HNF: Hepatocyte nuclear factor.
- Citation: Chen ML, Lee KD, Huang HC, Tsai YL, Wu YC, Kuo TM, Hu CP, Chang C. HNF-4α determines hepatic differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells from bone marrow. World J Gastroenterol 2010; 16(40): 5092-5103
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v16/i40/5092.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v16.i40.5092