Copyright
copy;2010 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Oct 21, 2010; 16(39): 4932-4937
Published online Oct 21, 2010. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v16.i39.4932
Published online Oct 21, 2010. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v16.i39.4932
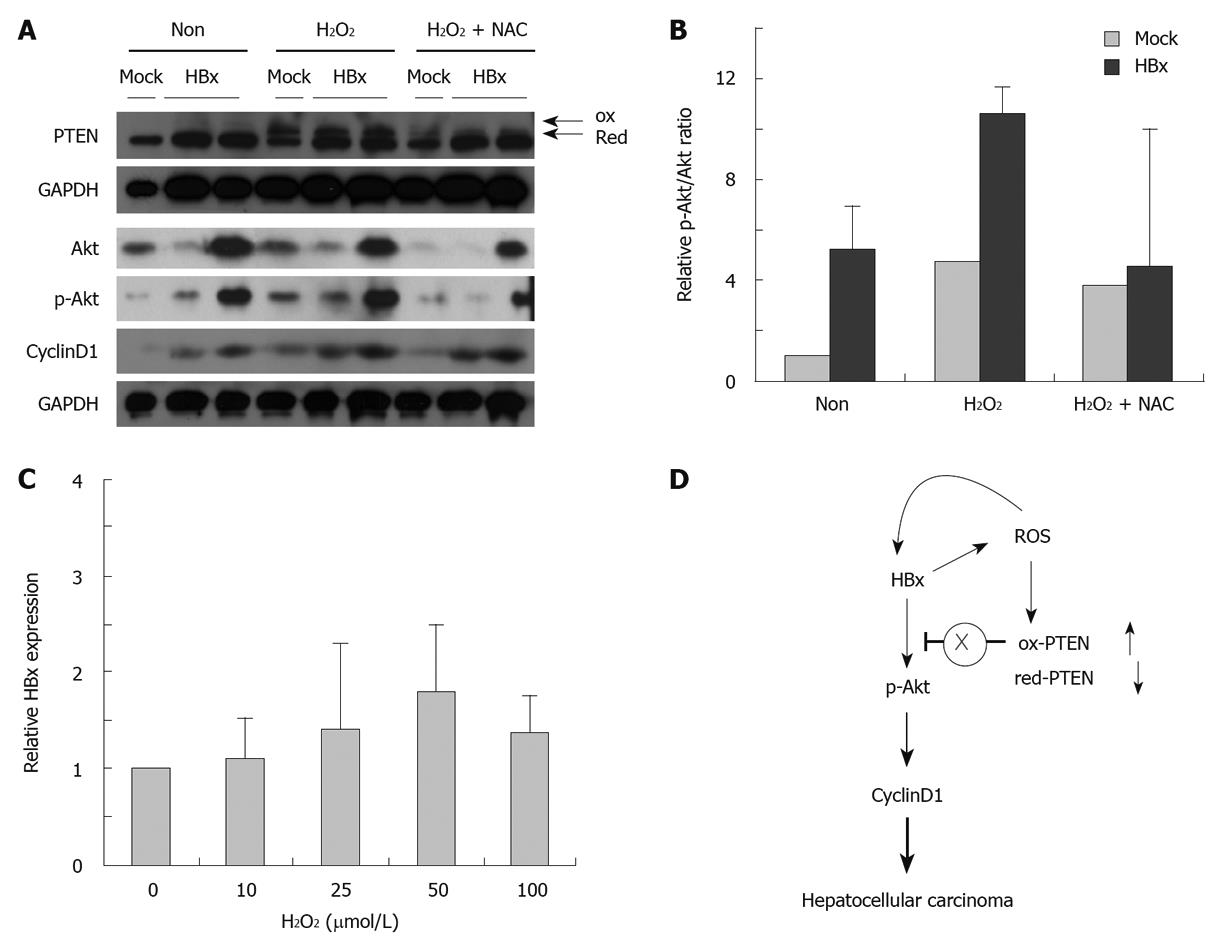
Figure 4 Effect of reactive oxygen species on phosphatase and tensin homolog oxidation, Akt pathway and hepatitis B virus X-protein expression.
A, B: H2O2 treatment induced phosphatase and tensin homolog (PTEN) oxidation and activation of Akt pathway (increased relative p-Akt/total Akt ratio, cyclin D1 expression). Reactive oxygen species (ROS) scavenging through N-acetylcysteine (NAC) treatment reduced PTEN oxidation and Akt pathway; C: ROS effect on hepatitis B virus X-protein (HBx) expression, by quantitative reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction; D: Proposed scheme for ROS effect for activating Akt pathway via PTEN oxidation in HBx-induced hepatocarcinogenesis.
-
Citation: Ha HL, Yu DY. HBx-induced reactive oxygen species activates hepatocellular carcinogenesis
via dysregulation of PTEN/Akt pathway. World J Gastroenterol 2010; 16(39): 4932-4937 - URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v16/i39/4932.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v16.i39.4932