Copyright
copy;2010 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Oct 21, 2010; 16(39): 4932-4937
Published online Oct 21, 2010. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v16.i39.4932
Published online Oct 21, 2010. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v16.i39.4932
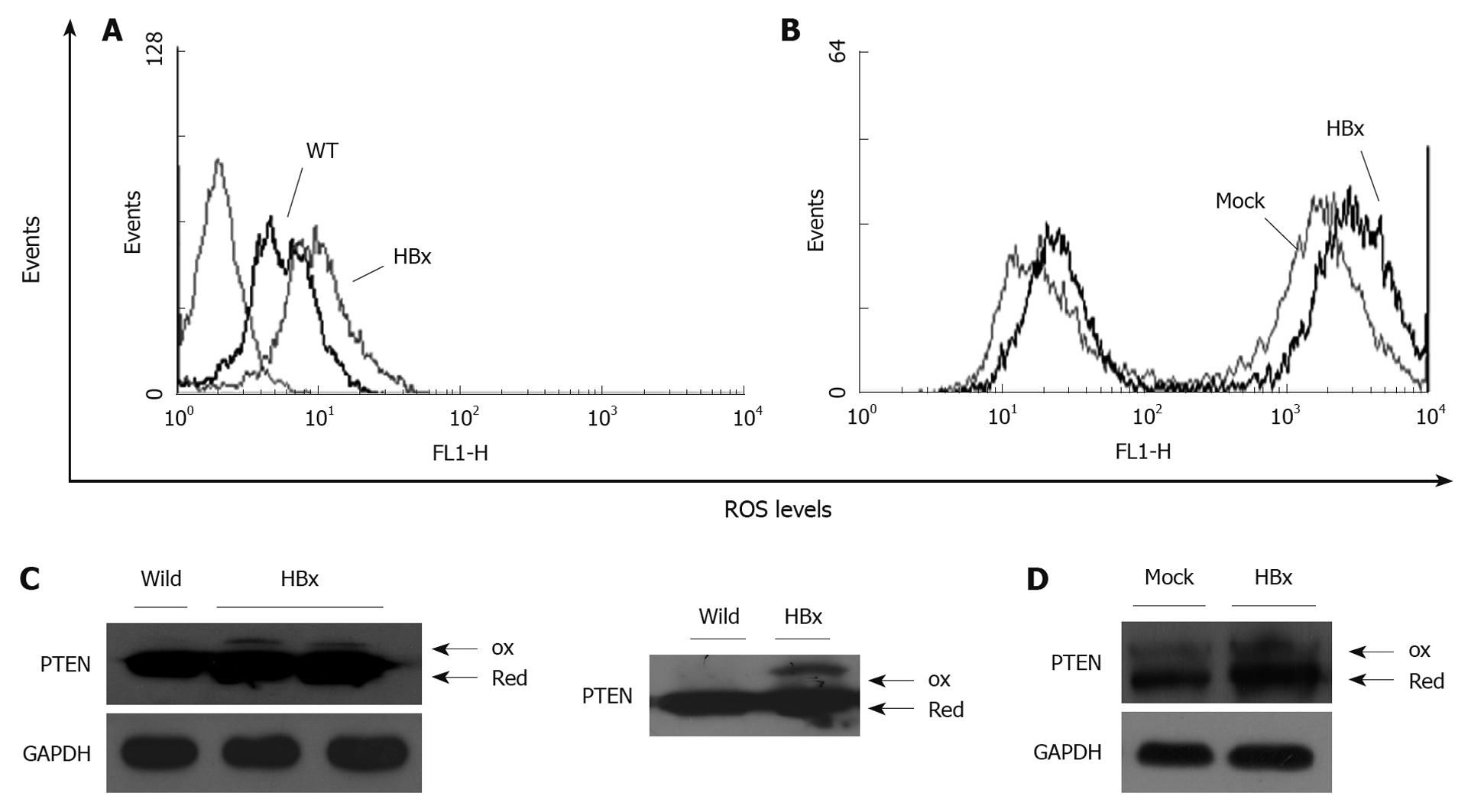
Figure 3 Effect of hepatitis B virus X-protein-induced endogenous reactive oxygen species and phosphatase and tensin homolog oxidation.
Endogenous reactive oxygen species (ROS) level was examined by flow cytometry. A, B: Increased production of ROS in hepatitis B virus X-protein (HBx) primary hepatocytes compared to the wild-type hepatocytes and HepG2-HBx compared to the Mock cells. Oxidized phosphatase and tensin homolog (PTEN) was detected by N-ethylmaleimide alkylation, and non-reducing sodium dodecyl sulfate polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis; C: In the upper panel, 20 μg protein was loaded, and for the lower panel, 50 μg was loaded; D: Parallel experiments were performed with extracts from HepG2-Mock and HBx cell lines.
-
Citation: Ha HL, Yu DY. HBx-induced reactive oxygen species activates hepatocellular carcinogenesis
via dysregulation of PTEN/Akt pathway. World J Gastroenterol 2010; 16(39): 4932-4937 - URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v16/i39/4932.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v16.i39.4932