Copyright
copy;2010 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Sep 28, 2010; 16(36): 4599-4604
Published online Sep 28, 2010. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v16.i36.4599
Published online Sep 28, 2010. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v16.i36.4599
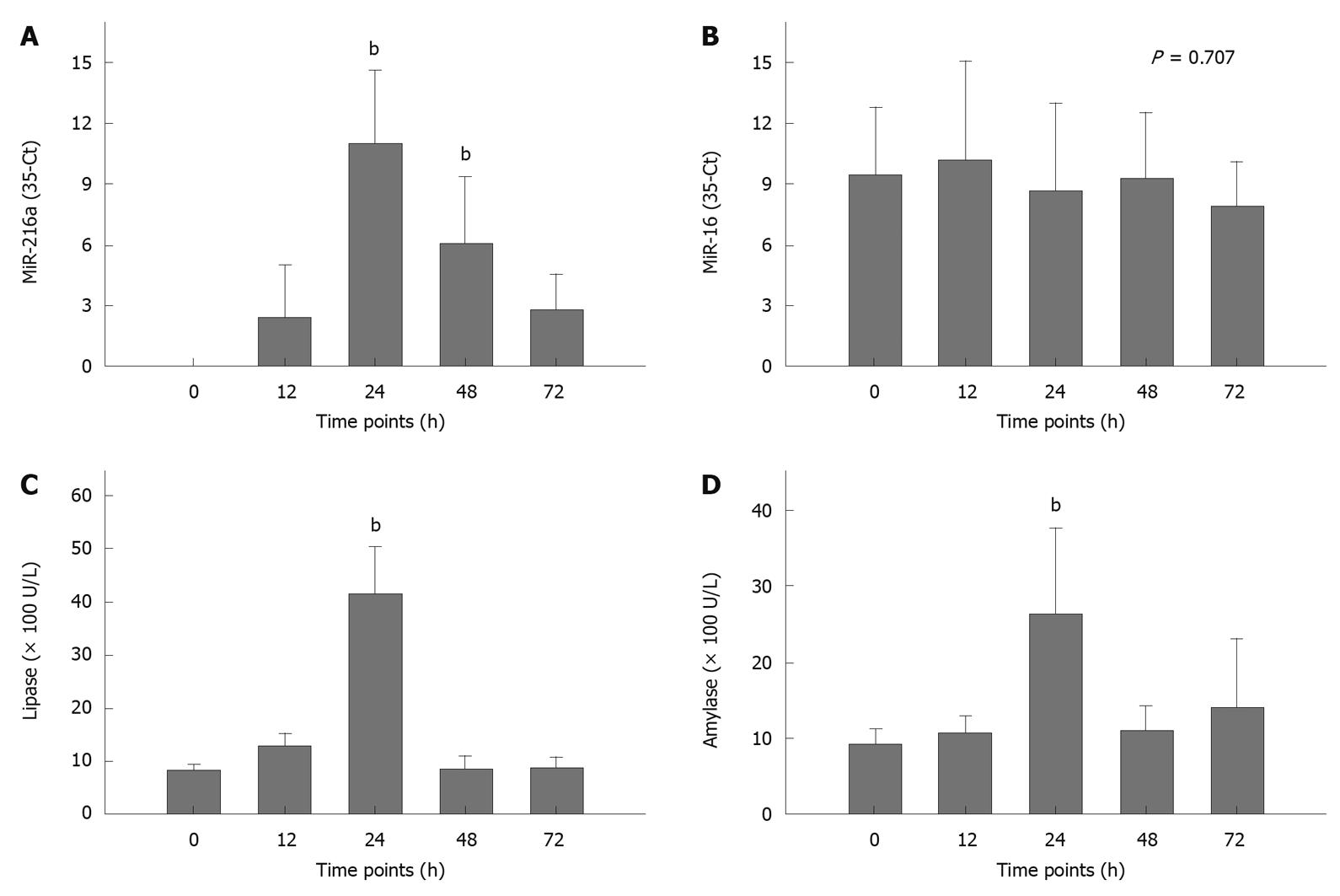
Figure 2 Plasma levels of miR-216a, miR-16, lipase, and amylase at different time points after induction of acute pancreatitis.
A: Production of plasma miR-216a was significantly increased 24 h after L-arginine administration and remained significantly higher until 48 h after administration (Kruskal-Wallis Test); B: The amount of plasma miR-16 remained unchanged across all time points (One-way ANOVA); C and D: Plasma lipase and amylase levels were significantly elevated 24 h after administration (Kruskal-Wallis Test). Data are presented as the mean and SD. Ten rats were studied at each time point. bP < 0.01 vs 0 h time point.
- Citation: Kong XY, Du YQ, Li L, Liu JQ, Wang GK, Zhu JQ, Man XH, Gong YF, Xiao LN, Zheng YZ, Deng SX, Gu JJ, Li ZS. Plasma miR-216a as a potential marker of pancreatic injury in a rat model of acute pancreatitis. World J Gastroenterol 2010; 16(36): 4599-4604
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v16/i36/4599.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v16.i36.4599