Copyright
copy;2010 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Sep 28, 2010; 16(36): 4541-4548
Published online Sep 28, 2010. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v16.i36.4541
Published online Sep 28, 2010. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v16.i36.4541
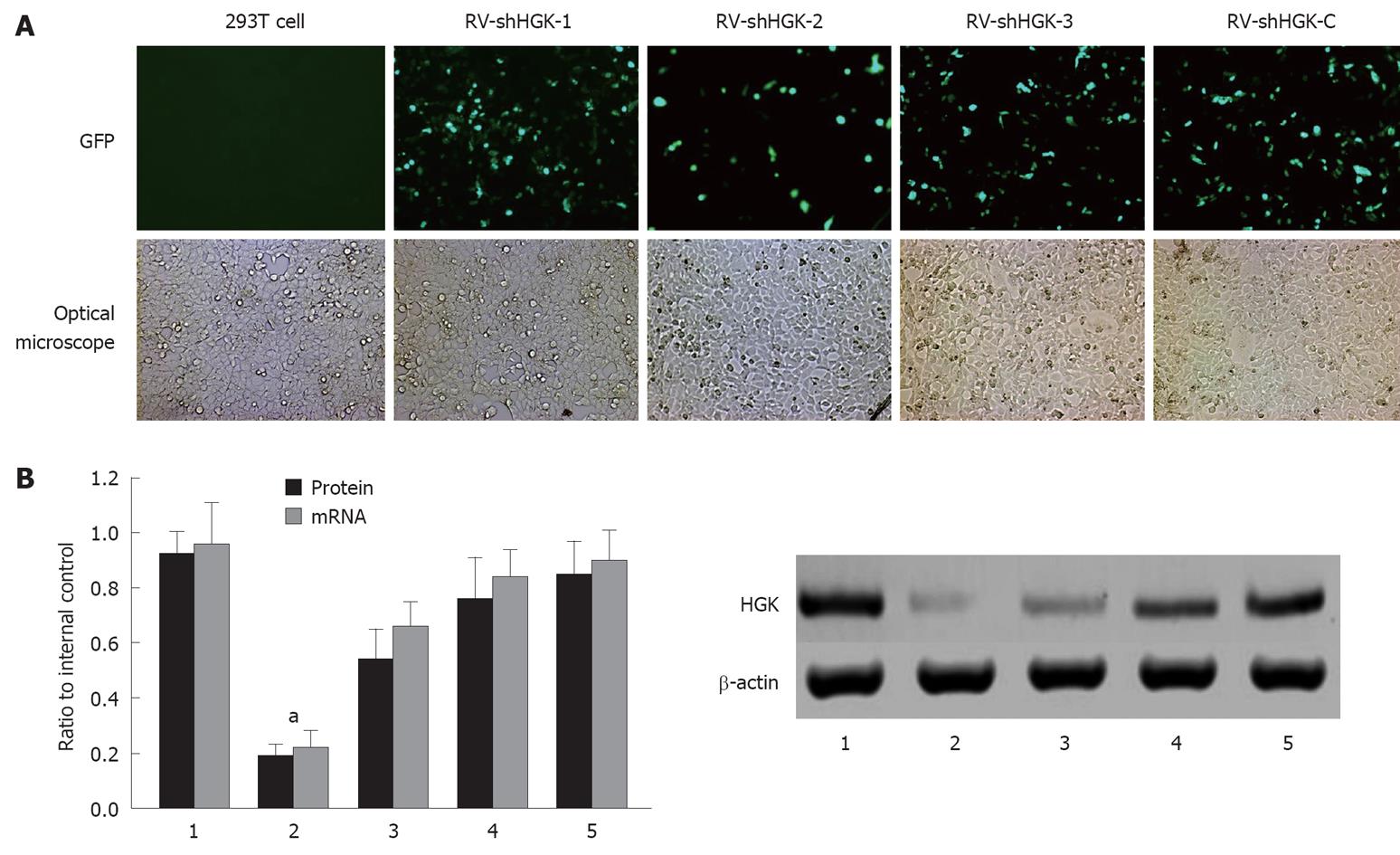
Figure 1 Selection of the most effective hepatocyte progenitor kinase-like kinase specific shRNA expression vector in 293T cells.
A: Phase contrast and GFP expression under a fluorescent microscope after 48 h in 293T cells; B: Protein mRNA and hepatocyte progenitor kinase-like kinase (HGK) levels after HepG2 cells were treated with different vectors detected by real-time reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction and Western boltting assay. The vector retrovirus mediating RNAi targeting of HGK (RV-shHGK)-1 significantly inhibited HGK expression in HepG2 cells, aP < 0.05 vs HepG2 cells and HepG2 cells transfected with RV-shHGK-C vector. 1: 293T cells; 2: Transfection of RV-shHGK-1 vector in 293T cells; 3: Transfection of RV-shHGK-2 vector; 4: Transfection of RV-shHGK-3 vector; 5: Transfection of RV-shHGK-C vector (original magnification × 200).
- Citation: Han SX, Zhu Q, Ma JL, Zhao J, Huang C, Jia X, Zhang D. Lowered HGK expression inhibits cell invasion and adhesion in hepatocellular carcinoma cell line HepG2. World J Gastroenterol 2010; 16(36): 4541-4548
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v16/i36/4541.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v16.i36.4541