Copyright
©2010 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Sep 14, 2010; 16(34): 4281-4290
Published online Sep 14, 2010. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v16.i34.4281
Published online Sep 14, 2010. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v16.i34.4281
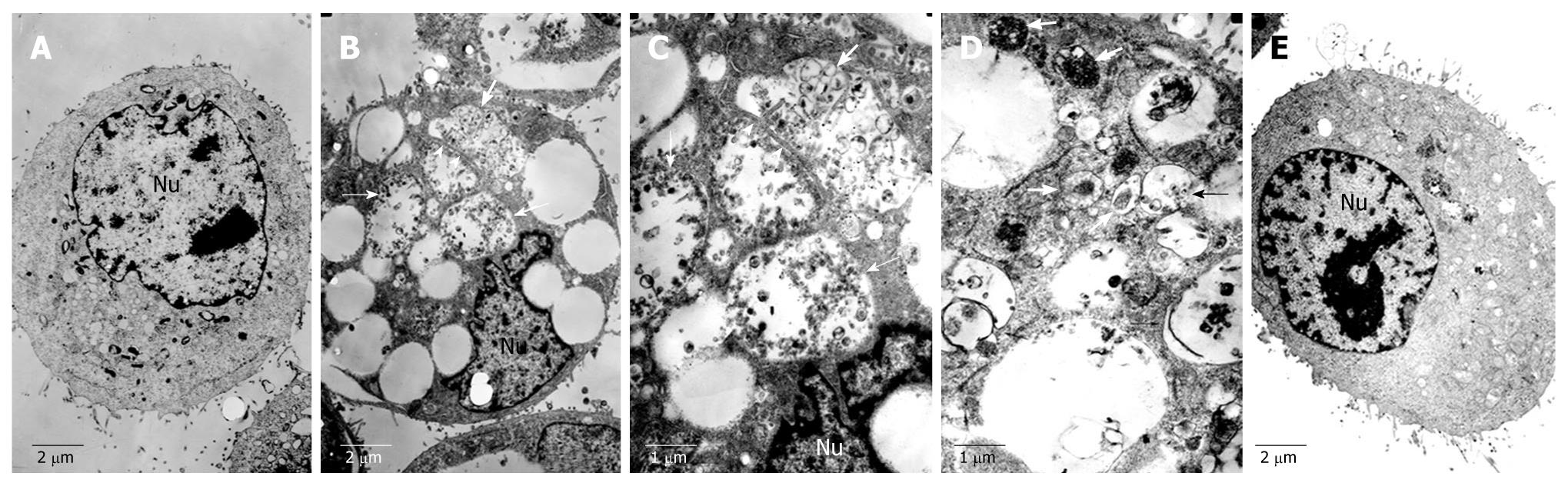
Figure 6 Transmission electron microscopy showing normal morphology of cytoplasm, cell organelles, and nuclei of HepG2 cells not treated with matrine (A), characteristic ultrastructural morphology of autophagy (B), double-membrane (C) and a large number of autophagic vacuoles (D) of HepG2 cells treated with matrine, and sharply decreased autophagic vacuoles (E) of HepG2 cells treated with combination of 3-MA and matrine (A, B, E, × 4000; C, D, × 8000).
Arrowheads represent double-membrane, thick arrows represent autophagosomes, and thin arrows represent autolysosomes. Nu: Nucleus.
- Citation: Zhang JQ, Li YM, Liu T, He WT, Chen YT, Chen XH, Li X, Zhou WC, Yi JF, Ren ZJ. Antitumor effect of matrine in human hepatoma G2 cells by inducing apoptosis and autophagy. World J Gastroenterol 2010; 16(34): 4281-4290
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v16/i34/4281.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v16.i34.4281