Copyright
copy;2010 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Sep 7, 2010; 16(33): 4180-4186
Published online Sep 7, 2010. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v16.i33.4180
Published online Sep 7, 2010. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v16.i33.4180
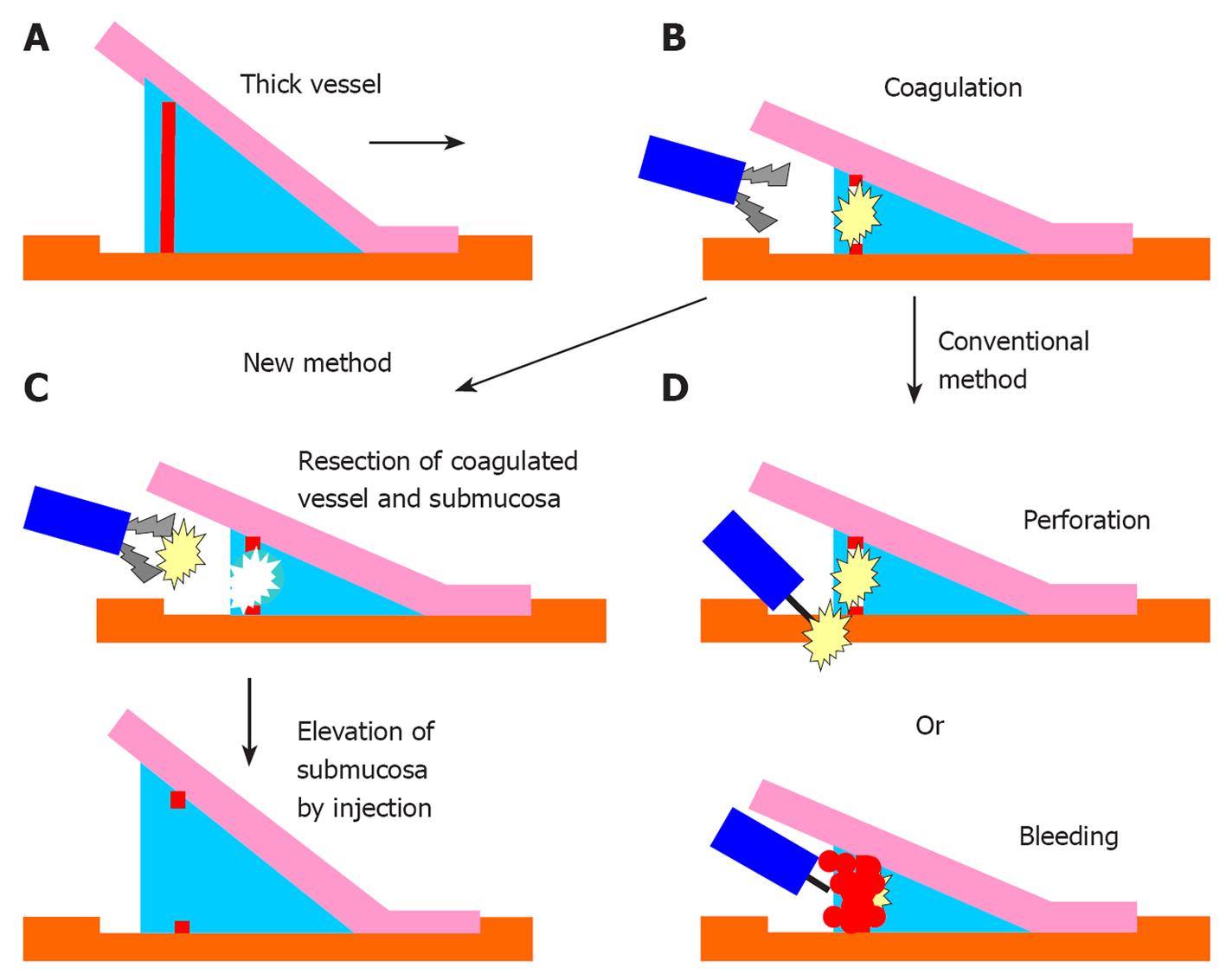
Figure 1 Schema of the efficacy of the new hemostatic forceps method.
A: A thick vessel is detected during the submucosal dissection; B: The thick vessel is coagulated using the hemostatic forceps. The vessel and surrounding submucosa become whitish, and the submucosa becomes less elevated; C: In the new method, the coagulated vessel is removed using the hemostatic forceps and the surrounding submucosa is also dissected. After the treatment, the submucosa is elevated by injecting it with hyaluronic acid and glycerin; D: In the conventional use of hemostatic forceps, perforation can occur because of inadequate submucosal elevation; moreover, hemorrhage can occur from the coagulated vessel while dissecting it with a knife.
- Citation: Yoshida N, Naito Y, Kugai M, Inoue K, Wakabayashi N, Yagi N, Yanagisawa A, Yoshikawa T. Efficient hemostatic method for endoscopic submucosal dissection of colorectal tumors. World J Gastroenterol 2010; 16(33): 4180-4186
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v16/i33/4180.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v16.i33.4180