Copyright
copy;2010 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Sep 7, 2010; 16(33): 4152-4158
Published online Sep 7, 2010. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v16.i33.4152
Published online Sep 7, 2010. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v16.i33.4152
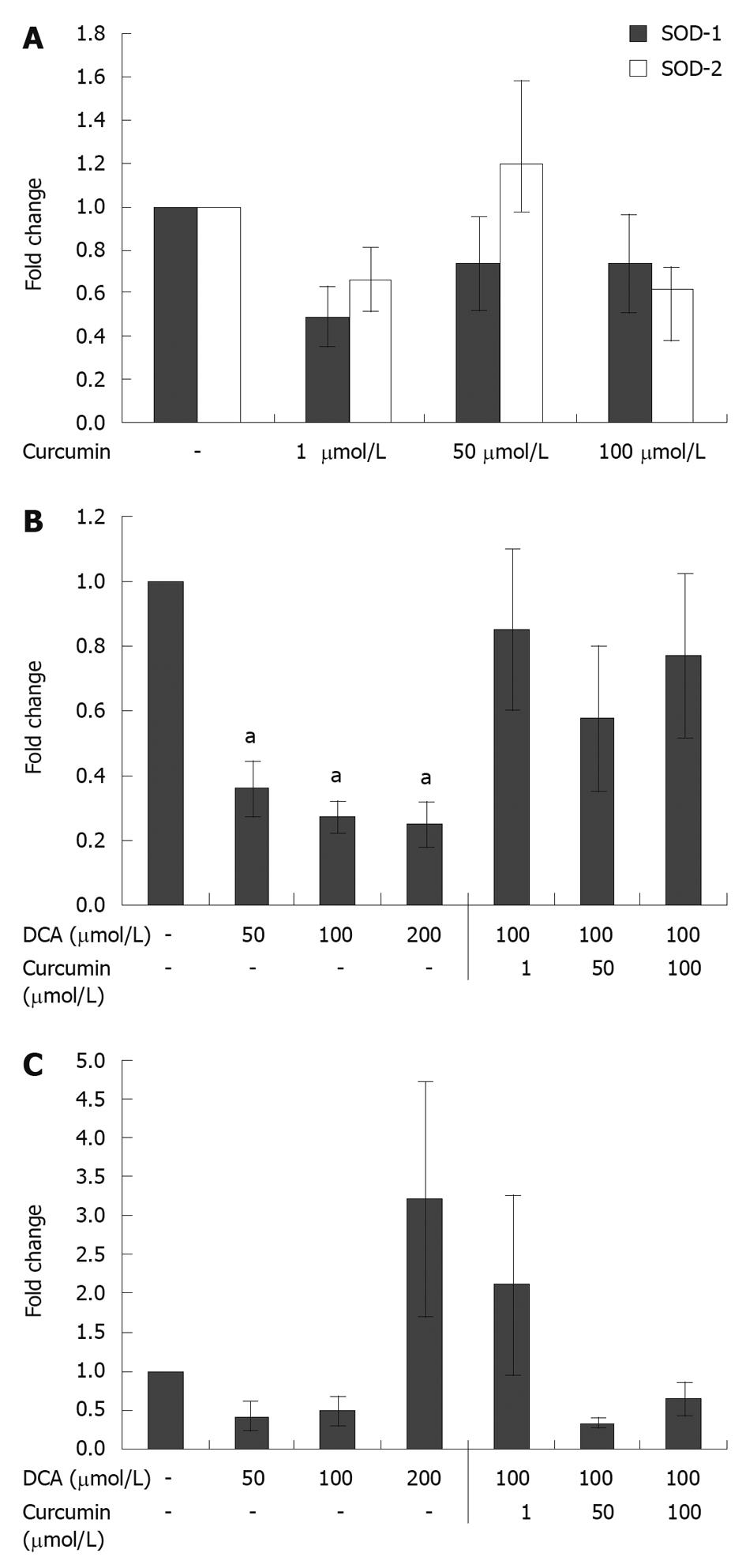
Figure 3 Effect of curcumin and bile acid on superoxide dismutase gene expression.
A: Effect of curcumin on superoxide dismutase (SOD)-1 and SOD-2 gene expression. HET-1A cells in 6-well plates at a density of 1.5 × 105 cells per well incubated with curcumin for 24 h did not show a significant impact on SOD-1 or SOD-2 gene expression. Error bars: mean ± SD (n = 4); B: Effect of curcumin and bile acid on SOD-1 gene expression. HET-1A cells in 6-well plates at a density of 1.5 × 105 cells per well incubated with deoxycholic acid (DCA) for 24 h showed a significant decrease in SOD-1 expression. When DCA treatment at 100 μmol/L was combined with curcumin the suppression in SOD-1 expression was alleviated. Error bars: mean ± SD (n = 4). aP < 0.05 vs vehicle control; C: Effect of curcumin and bile acid on SOD-2 gene expression. HET-1A cells in 6-well plates at a density of 1.5 × 105 cells per well incubated with deoxycholic acid (DCA) for 24 h showed a significant increase in SOD-2 expression at a DCA concentration of 200 μmol/L. The combined treatment of DCA and curcumin showed reduced expression of SOD-2 at concentrations ≥ 50 μmol/L. Error bars: mean ± SD (n = 4).
- Citation: Bower MR, Aiyer HS, Li Y, Martin RC. Chemoprotective effects of curcumin in esophageal epithelial cells exposed to bile acids. World J Gastroenterol 2010; 16(33): 4152-4158
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v16/i33/4152.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v16.i33.4152