Copyright
©2010 Baishideng.
World J Gastroenterol. Aug 14, 2010; 16(30): 3731-3742
Published online Aug 14, 2010. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v16.i30.3731
Published online Aug 14, 2010. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v16.i30.3731
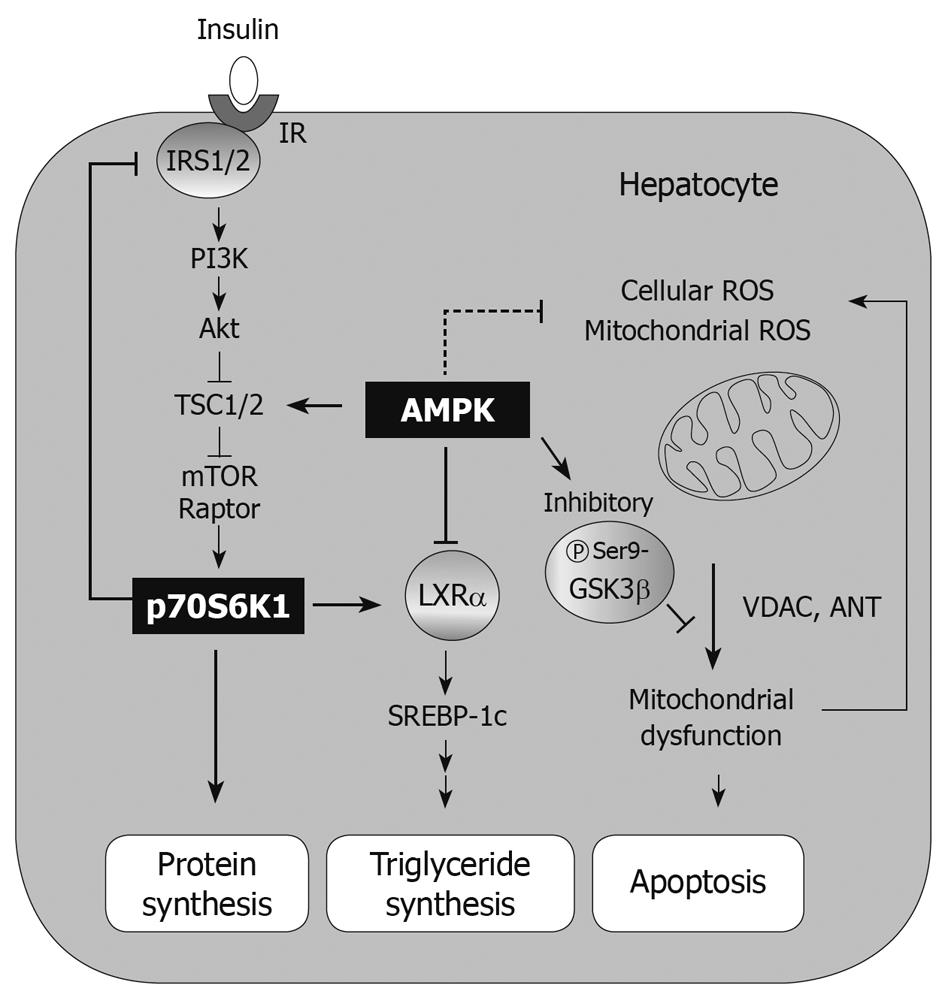
Figure 4 Dual regulation of fuel metabolism and cell viability by adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase.
The adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase (AMPK)-S6 kinase-1 (S6K1) pathway regulates metabolic signaling flow. In addition, AMPK controls the redox-state and mitochondrial function, therefore its activation protects cells from apoptosis. AMPK is the key molecule to bridge the gap between fuel metabolism and hepatocyte viability. IR: Insulin receptor; IRS1: Insulin receptor substrate-1; PI3K: Phosphoinositide-3 kinase; TSC1: Tuberous sclerosis complex 1; ROS: Reactive oxygen species; mTOR: Mammalian target of rapamycin; LXRα: Liver X receptor-α; GSK3β: Glycogen synthase kinase 3β; SREBP-1c: Sterol regulatory element, binding protein-1c; VDAC: Voltage-activated anion channel; ANT: Adenine nucleotide translocator.
- Citation: Yang YM, Han CY, Kim YJ, Kim SG. AMPK-associated signaling to bridge the gap between fuel metabolism and hepatocyte viability. World J Gastroenterol 2010; 16(30): 3731-3742
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v16/i30/3731.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v16.i30.3731