Copyright
©2010 Baishideng.
World J Gastroenterol. Jul 28, 2010; 16(28): 3584-3591
Published online Jul 28, 2010. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v16.i28.3584
Published online Jul 28, 2010. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v16.i28.3584
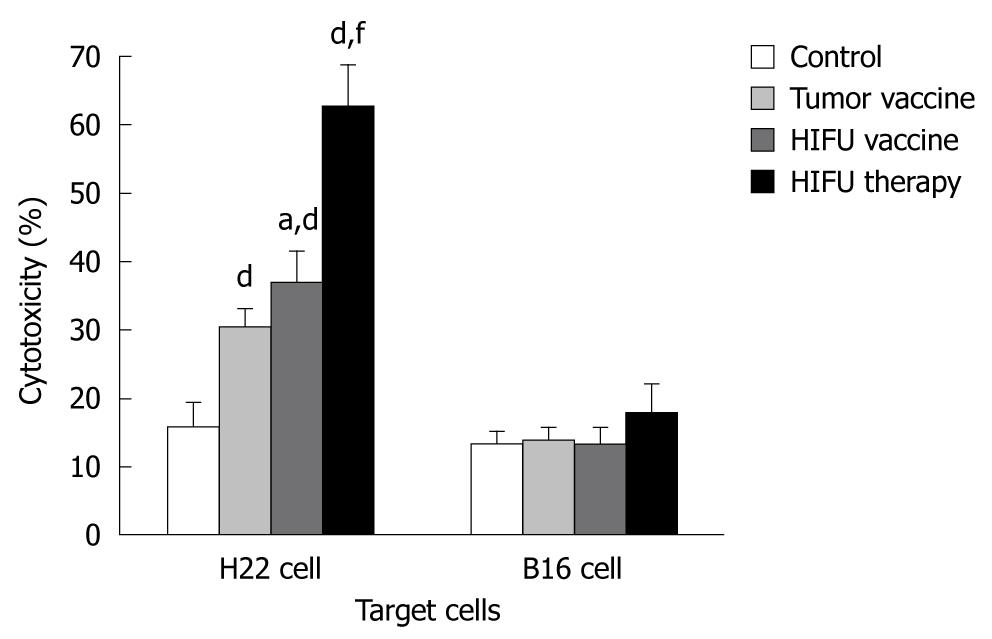
Figure 1 Cytotoxic activity of cytotoxic T lymphocytes against either H22 or B16 tumor cells in vitro at 10:1 effector:target ratio in the vaccinated and high-intensity focused ultrasound-treated mice.
Naïve mice were vaccinated with high-intensity focused ultrasound (HIFU)-generated and tumor-generated vaccines, and saline alone once a week for 2 wk. The mice bearing H22 tumors were also treated with HIFU ablation. The vaccinated animals were sacrificed 7 d after the 2nd vaccination, and the HIFU-treated mice were sacrificed 15 d after HIFU therapy. The spleens were harvested, and single cell suspensions were generated. The splenic lymphocytes were then co-cultured with either H22 or B16 cells for 24 h. The cytotoxicity of the cytotoxic T lymphocytes was determined with a 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide assay in each group after 2 h co-incubation. aP < 0.05 vs the tumor-generated vaccine; dP < 0.001 vs the control; fP < 0.001 vs the HIFU- and tumor-generated vaccines.
- Citation: Zhang Y, Deng J, Feng J, Wu F. Enhancement of antitumor vaccine in ablated hepatocellular carcinoma by high-intensity focused ultrasound. World J Gastroenterol 2010; 16(28): 3584-3591
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v16/i28/3584.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v16.i28.3584